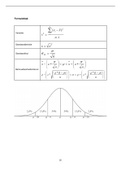
Summary HEP4205
Implementation & Evaluation
Introduction lecture 1
Case 1: Does the puzzle piece fit? 6
Case 2: Implementation: more complex than you thought? 18
Case 3: Vitality at Work! Implementing health promotion in the workplace 27
Case 4: Process and effect evaluation: (how) does it work? 40
Case 5: Economic evaluation to the rescue 49
Lecture: Dynamic systems 56
,Introduction lecture
D&I = dissemination and implementation plan
Limited impact in real life
• EBI based on theories and empirical research
• Tested in efficacy trials (controlled and thus focus on internal validity)
• Compared with drug developed in medical research:
o Tested under highly artificial conditions ≠ implementation in real life
o Tested with motivated people and strict inclusion criteria ≠ effectiveness in real life
Features of EBIs
• Difficult to understand advantages; how and under which circumstances will it work?
• Effects not clearly and immediately visible for users
• Programmes are often complex
o With many elements (e.g. a lifestyle programme or workplace)
when is this EBI ‘completely’ used?
o Is it allowed to delete or adopt?
Because complexity EBIs
• More likely to have elements that are incompatible with setting
• Evokes resistance
• Or attempts to adapt the EBI
Gap between research and practice
• Researchers
o Tradition-bound practitioners insist on practicing their way
o They claim to know their target group best
• Practitioners
o The lack of relevance and fit of evidence
o Barriers to implementation
Funnel by Green
It takes around 17 years for knowledge that we have to be implemented into practice and it is
funnel shaped because it gets adapted.
1
, Dissemination and implementation are of concern of scientists
Implementation science = the scientific study of methods to promote the systematic uptake of
research findings and other evidence-based practices into routine practice. It includes the study
of influences on healthcare professionals and organizational behaviour.
Definitions D&I
• Dissemination = the targeted distribution of information and intervention materials to a
specific public health audience
• Implementation = increasing the integration of EBIs into routing real-world practices
→ Different authors use different definitions and therefore we use the definitions of
Brownson et al. 2018.
Framework: steps
2
Implementation & Evaluation
Introduction lecture 1
Case 1: Does the puzzle piece fit? 6
Case 2: Implementation: more complex than you thought? 18
Case 3: Vitality at Work! Implementing health promotion in the workplace 27
Case 4: Process and effect evaluation: (how) does it work? 40
Case 5: Economic evaluation to the rescue 49
Lecture: Dynamic systems 56
,Introduction lecture
D&I = dissemination and implementation plan
Limited impact in real life
• EBI based on theories and empirical research
• Tested in efficacy trials (controlled and thus focus on internal validity)
• Compared with drug developed in medical research:
o Tested under highly artificial conditions ≠ implementation in real life
o Tested with motivated people and strict inclusion criteria ≠ effectiveness in real life
Features of EBIs
• Difficult to understand advantages; how and under which circumstances will it work?
• Effects not clearly and immediately visible for users
• Programmes are often complex
o With many elements (e.g. a lifestyle programme or workplace)
when is this EBI ‘completely’ used?
o Is it allowed to delete or adopt?
Because complexity EBIs
• More likely to have elements that are incompatible with setting
• Evokes resistance
• Or attempts to adapt the EBI
Gap between research and practice
• Researchers
o Tradition-bound practitioners insist on practicing their way
o They claim to know their target group best
• Practitioners
o The lack of relevance and fit of evidence
o Barriers to implementation
Funnel by Green
It takes around 17 years for knowledge that we have to be implemented into practice and it is
funnel shaped because it gets adapted.
1
, Dissemination and implementation are of concern of scientists
Implementation science = the scientific study of methods to promote the systematic uptake of
research findings and other evidence-based practices into routine practice. It includes the study
of influences on healthcare professionals and organizational behaviour.
Definitions D&I
• Dissemination = the targeted distribution of information and intervention materials to a
specific public health audience
• Implementation = increasing the integration of EBIs into routing real-world practices
→ Different authors use different definitions and therefore we use the definitions of
Brownson et al. 2018.
Framework: steps
2