Section 1
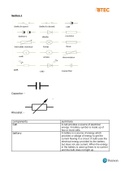
Capacitor -
Rheostat -
components summary
Cell A cell provides a source of electrical
energy. A battery symbol is made up of
two or more cells.
battery A battery is a source of energy which
provides a voltage of energy to get the
current flowing in a circuit. A bulb uses the
electrical energy provided by the battery,
but does not use current. When the energy
in the battery is used up there is no current
and the bulb does not light up.
, switch A switch is an electrical component that
can disconnect or connect the conducting
path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the
electric current or diverting it from one
conductor to another.
Filament lamp A filament lamp is a common type of light
bulb. It contains a thin coil of wire called
the filament. This heats up when an
electric current passes through it, and
produces light as a result.
Fixed resistor Fixed value resistors have a defined ohmic
resistance and are not adjustable. Fixed
resistors are the most commonly used
resistors and in general one of the most
used electronic components.
thermistor The Thermistor is a solid state
temperature sensing device which acts a
bit like an electrical resistor but is
temperature sensitive.
LED (light emitting diode) It is a semiconductor light source that
emits light when current flows through it.
LDR (light dependent resistor) LDR is a component that has a (variable)
resistance that changes with the light
intensity that falls upon it. This allows them
to be used in light sensing circuits.
rheostat adjustable resistor used in applications that
require the adjustment of current or the
varying of resistance in an electric circuit.
capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical
component used to store energy
electrostatically in an electric field. A
capacitor stores energy in the form of an
electrostatic field between its plates.
voltmeter It is an instrument used for measuring
electrical potential difference between two
points in an electric circuit.
ammeter is a measuring device used to measure the
electric current in a circuit.
· current (ampere)
- It is the rate of flow of charge or in simple terms it is the flow of electrical
charge.
- In wires, the actual charge carriers are negatively charged electrons.
-The symbol of current is I
-The unit of current is amps.
· potential difference (volt)
2
BTEC Assignment Brief v1.0
BTEC Internal Assessment QDAM January 2015
, -It is the work done per unit charge or in simple terms it is the energy released
in transfer of a unit quantity of electricity from one point to another.
-The symbol of potential difference is V
-The unit of potential difference is volts.
· electrical charge (coulomb)
- It is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when
placed in an electromagnetic field or in simple terms it is a positive charge that
is attracted to a negative charge.
-The symbol of electric charge is Q
-The unit of electric charge is coulombs.
· resistance (ohm)
-It is the opposition to the flow of current in an electric circuit or in other words
it is the measure of the opposition of current flow
-The symbol of resistance is R
-The unit of resistance is ohms.
· conductance (Siemen)
-It is the degree to which an object conducts electricity calculated as the ratio
of the current which flows to the potential or in other words it is how good a
material can conduct electricity
-The symbol of conductance is G
-The unit of conductance is Siemen.
· electrical power (watt)
-It is the rate per unit time at which energy is transferred or in simple terms it
is the transfer by electrical circuit.
-The symbol of electrical power is P
-The unit of electrical power is watts.
· capacitance (farad and sub-units)
-It Is the ability of a system to store an electric charge.
-The symbol of capacitance is C
-The unit of capacitance is farads.
· electromotive force (EMF)
- Amount of energy that comes into circuit per unit charge
-The symbol of EMF is V
-The unit of EMF is volts.
Section2-
· Energy supplied:
-W=VxIxt
-example:
3
BTEC Assignment Brief v1.0
BTEC Internal Assessment QDAM January 2015
Capacitor -
Rheostat -
components summary
Cell A cell provides a source of electrical
energy. A battery symbol is made up of
two or more cells.
battery A battery is a source of energy which
provides a voltage of energy to get the
current flowing in a circuit. A bulb uses the
electrical energy provided by the battery,
but does not use current. When the energy
in the battery is used up there is no current
and the bulb does not light up.
, switch A switch is an electrical component that
can disconnect or connect the conducting
path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the
electric current or diverting it from one
conductor to another.
Filament lamp A filament lamp is a common type of light
bulb. It contains a thin coil of wire called
the filament. This heats up when an
electric current passes through it, and
produces light as a result.
Fixed resistor Fixed value resistors have a defined ohmic
resistance and are not adjustable. Fixed
resistors are the most commonly used
resistors and in general one of the most
used electronic components.
thermistor The Thermistor is a solid state
temperature sensing device which acts a
bit like an electrical resistor but is
temperature sensitive.
LED (light emitting diode) It is a semiconductor light source that
emits light when current flows through it.
LDR (light dependent resistor) LDR is a component that has a (variable)
resistance that changes with the light
intensity that falls upon it. This allows them
to be used in light sensing circuits.
rheostat adjustable resistor used in applications that
require the adjustment of current or the
varying of resistance in an electric circuit.
capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical
component used to store energy
electrostatically in an electric field. A
capacitor stores energy in the form of an
electrostatic field between its plates.
voltmeter It is an instrument used for measuring
electrical potential difference between two
points in an electric circuit.
ammeter is a measuring device used to measure the
electric current in a circuit.
· current (ampere)
- It is the rate of flow of charge or in simple terms it is the flow of electrical
charge.
- In wires, the actual charge carriers are negatively charged electrons.
-The symbol of current is I
-The unit of current is amps.
· potential difference (volt)
2
BTEC Assignment Brief v1.0
BTEC Internal Assessment QDAM January 2015
, -It is the work done per unit charge or in simple terms it is the energy released
in transfer of a unit quantity of electricity from one point to another.
-The symbol of potential difference is V
-The unit of potential difference is volts.
· electrical charge (coulomb)
- It is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when
placed in an electromagnetic field or in simple terms it is a positive charge that
is attracted to a negative charge.
-The symbol of electric charge is Q
-The unit of electric charge is coulombs.
· resistance (ohm)
-It is the opposition to the flow of current in an electric circuit or in other words
it is the measure of the opposition of current flow
-The symbol of resistance is R
-The unit of resistance is ohms.
· conductance (Siemen)
-It is the degree to which an object conducts electricity calculated as the ratio
of the current which flows to the potential or in other words it is how good a
material can conduct electricity
-The symbol of conductance is G
-The unit of conductance is Siemen.
· electrical power (watt)
-It is the rate per unit time at which energy is transferred or in simple terms it
is the transfer by electrical circuit.
-The symbol of electrical power is P
-The unit of electrical power is watts.
· capacitance (farad and sub-units)
-It Is the ability of a system to store an electric charge.
-The symbol of capacitance is C
-The unit of capacitance is farads.
· electromotive force (EMF)
- Amount of energy that comes into circuit per unit charge
-The symbol of EMF is V
-The unit of EMF is volts.
Section2-
· Energy supplied:
-W=VxIxt
-example:
3
BTEC Assignment Brief v1.0
BTEC Internal Assessment QDAM January 2015