Lecture 15-17 – EvoDevo
EvoDevo→ Compare developmental processes to infer ancestral relationships and
understand how developmental processes evolved
Why look at development?
Because the body plan is established during development!
A single cell (zygote) contains all information on the adult body plan
Body plans enroll step by step
• Signaling gradients, axis formation
• Cell differentiation & fate determination
• Proliferation, apoptosis, cell migration
• Modularity, segmentation
• Organogenesis
• Maturation, timing (heterochrony), neoteny
Founding fathers of EvoDevo
- Ernst Haeckel, 1866
- Biogenetic law
• “Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny”
- Karl Ernst von Baer, 1828
• “The embryo successively adds the organs
that characterize the animal classes in the
ascending scale.”
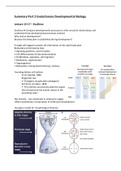
Not entirely... but similarities in embryonic stages
reflect evolutionary conservation of embryonic development
Hourglass model for morphological diversity
,The genetic toolbox for development is evolutionary extremely conserved
• How is this conservation reflected in developmental processes?
• How does this conserved toolbox allow the large diversity in body plans?
Evolution of additional transcription factors and signaling pathway genes
Gene expression patterns & signaling cascades are critical to differentiate developmental
processes: when, where, how much.
,Tissue patterning & body axes
Direction essential to coordinate organs and
tissues!
How are the body axes initiated?
• Anterior & posterior (A-P) = front & rear
• Dorsal & ventral (D-V) = back & belly side
• Left & right (Bilateria)
Drosophila: model for axis formation
Drosophila? YES!
• Many basal embryonic features pre-date the split
between Protostomes and Deuterostomes
• The developmental molecular toolbox also pre-dates
the split
• Homologous genes between Drosophila and
mammals
• Nobel prize 1995, genetic control of embryonic
development in Drosophila
The egg chamber of the Drosophila ovariole
- Developing eggs are provisioned with maternal mRNA during oogenesis
- Zygotes typically do not commence
transcription until after 2-3 divisions
- Drosophila egg has already a dorsal-
ventral axis induced by its mother!
Bicoid (Bcd) forms an A-P gradient
Bicoid is essential for establishing the A-P axis
Bicoid is the morphogen for head and thorax
development
Morphogen: compound with a non-uniform
distribution establishing positions of specialized
cell types and tissues
, Transplantation of Bicoid-containing cells induces ectopic anterior identity
• Anterior and posterior become thorax, the head is formed in the middle
• Ectopic: away from the normal position
Morphogens induce a signaling cascade that controls pattern formation
• Bicoid suppresses Caudal in the anterior part
• Nanos suppresses Hunchback in the posterior part
Dorso-ventral axis:
activation of Dorsal by the Toll-Spätzle pathway
Spätzle is the morphogen for dorso-ventral axis
formation
Phosphorylation of Dorsal at the ventral region
prompts translocation to the nucleus
Dorsal binds to DNA and regulates transcription of
target genes in a concentration-dependent manner
•Decapentaplegic (DPP)
•Sog
•Snail