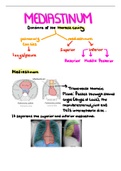
1 ON TRANSPORT
1 Solute diffusion across cell membranes
There is constant traffic across cell membranes
cells derive nutrients from extracellular fluid
Oz supply
Supply of substrate for cellular metabolism Cglucose
Removal of CO2 waste products
Diffusion definition The net movement of a substance
from a region of high concentration to an area of low
concentration down a concentration gradient
There is no
energy source required passivediffusion
Results from random thermal movement of molecules
, Factors affecting the rate of diffusion include
Concentration gradient
Membrane permeability of the substance
cell membrane is selectively permeable
Fattyacids steroid hormones O2 CO2
readily diffuse
ions and proteins lipid insoluble less
readily diffuse
tons diffuse better than predicted due to carrier molecules
Membrane voltagegradients
cell negative inside us outside
cations attracted in electrostatically
N ET ion flux L to combined electrical and concentration
gradients
Molecular weight of diffusing substance
small molecules diffuse faster
diffuse more
large molecules
slowly
Diffusion distance
limited to
100µm
Membrane surface area
Rate of diffusion membrane surface area
Temperature
Temp d rate of diffusion C think fever
1 Solute diffusion across cell membranes
There is constant traffic across cell membranes
cells derive nutrients from extracellular fluid
Oz supply
Supply of substrate for cellular metabolism Cglucose
Removal of CO2 waste products
Diffusion definition The net movement of a substance
from a region of high concentration to an area of low
concentration down a concentration gradient
There is no
energy source required passivediffusion
Results from random thermal movement of molecules
, Factors affecting the rate of diffusion include
Concentration gradient
Membrane permeability of the substance
cell membrane is selectively permeable
Fattyacids steroid hormones O2 CO2
readily diffuse
ions and proteins lipid insoluble less
readily diffuse
tons diffuse better than predicted due to carrier molecules
Membrane voltagegradients
cell negative inside us outside
cations attracted in electrostatically
N ET ion flux L to combined electrical and concentration
gradients
Molecular weight of diffusing substance
small molecules diffuse faster
diffuse more
large molecules
slowly
Diffusion distance
limited to
100µm
Membrane surface area
Rate of diffusion membrane surface area
Temperature
Temp d rate of diffusion C think fever