From Molecule to Mind - Neurobiology
Chemical Synapses
In disease these structures may
change.
Neuromascular junction: pair of synaptic vesicles, between vesicles and between the membrane
there is stuff to keep it strong.
The junction has multiple release sites.
Endosomes: elongated vesicles and in this, endocytic vesicles fuse and new vesicles bud off and fill
up with neurotransmitter.
Different synapses: have different release probability and this plays an important role in the ability of
the brain to process information and store/retrieve it. The difference in release probability can be
explained by morphological and functional differences between synapses and their ability to adjust.
Release probability: how likely is it that a vesicle fuses to activate the postsynaptic side?
This may be different in different synapses.
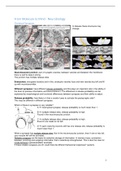
Which of these 4 synapses is very reliable?
A most typical synapse; release probability is much lower than 1.
B multiple release sites; release probability is high.
Found in the neuromuscular junction.
C multiple release sites; release probability is high.
B and C are made to not fail!
D each receiving neurons still has one release site; release probability is
much lower than 1.
When a synapse has multiple release sites, like in the neuromuscular junction, than if one or two fail,
your muscle will still be activated.
Reliable synapses are the basis for selective storage of information memory trace; connection
between incoming and outgoing information that is selectively strengthened. This is also the case for
innate behavior (goose/predator example).
If these reliable synapses are off, could there be different behavioral responses? (autism).
1
, Release probability in single synapse: really small, typical CNS synapses may have only 3 vesicles.
They cannot sustain high frequency for long.
Release probability is below 0.2 1 in 5 AP will lead to depolarization on the postsynaptic
site.
The summation of excitation and inhibition has to be in favor of excitation.
“Behavior is overcoming inhibition.”
Even in single synapses there is a yes or no release or no release of vesicles. This
variation determines whether there is an input on another neuron.
In the absence of stimulation there can be single (spontaneous) events of release.
Many synapses have a release probability of just below 0.2;
these are the “single” synapses in the CNS.
6 1 2 3 4 5
1 If you put 2 AP in close succession, the release probability of the synapse goes up. Release of
a vesicle becomes much higher when an AP has just arrived. For a short duration, this
synapse is very reliable (within ms).
2 If an AP arrives a little later, the release probability decreases again.
3 If you put many stimuli in a row (AP), the release probability first increases and then decreases
again, because the synapse runs out of vesicles.
4 If you have gone through an episode like this (like LTP stimulation), some time later the release
probability is will become 1 again, because new vesicles have been recruited.
5 This is not long-term and after some time it decreases again. This is called
post-tetanic stimulation.
6 This is not the case in the beginning, there was no high frequency stimulation. Therefore the
release probability here goes back to 0.5.
Post-tetanic stimulation: the increase in release probability takes a few ms.
LTP: the increase in release probability takes at least a few minutes. If you want to store the
information and compare the input with the stored information, you need this briefly higher release
probability.
2
Chemical Synapses
In disease these structures may
change.
Neuromascular junction: pair of synaptic vesicles, between vesicles and between the membrane
there is stuff to keep it strong.
The junction has multiple release sites.
Endosomes: elongated vesicles and in this, endocytic vesicles fuse and new vesicles bud off and fill
up with neurotransmitter.
Different synapses: have different release probability and this plays an important role in the ability of
the brain to process information and store/retrieve it. The difference in release probability can be
explained by morphological and functional differences between synapses and their ability to adjust.
Release probability: how likely is it that a vesicle fuses to activate the postsynaptic side?
This may be different in different synapses.
Which of these 4 synapses is very reliable?
A most typical synapse; release probability is much lower than 1.
B multiple release sites; release probability is high.
Found in the neuromuscular junction.
C multiple release sites; release probability is high.
B and C are made to not fail!
D each receiving neurons still has one release site; release probability is
much lower than 1.
When a synapse has multiple release sites, like in the neuromuscular junction, than if one or two fail,
your muscle will still be activated.
Reliable synapses are the basis for selective storage of information memory trace; connection
between incoming and outgoing information that is selectively strengthened. This is also the case for
innate behavior (goose/predator example).
If these reliable synapses are off, could there be different behavioral responses? (autism).
1
, Release probability in single synapse: really small, typical CNS synapses may have only 3 vesicles.
They cannot sustain high frequency for long.
Release probability is below 0.2 1 in 5 AP will lead to depolarization on the postsynaptic
site.
The summation of excitation and inhibition has to be in favor of excitation.
“Behavior is overcoming inhibition.”
Even in single synapses there is a yes or no release or no release of vesicles. This
variation determines whether there is an input on another neuron.
In the absence of stimulation there can be single (spontaneous) events of release.
Many synapses have a release probability of just below 0.2;
these are the “single” synapses in the CNS.
6 1 2 3 4 5
1 If you put 2 AP in close succession, the release probability of the synapse goes up. Release of
a vesicle becomes much higher when an AP has just arrived. For a short duration, this
synapse is very reliable (within ms).
2 If an AP arrives a little later, the release probability decreases again.
3 If you put many stimuli in a row (AP), the release probability first increases and then decreases
again, because the synapse runs out of vesicles.
4 If you have gone through an episode like this (like LTP stimulation), some time later the release
probability is will become 1 again, because new vesicles have been recruited.
5 This is not long-term and after some time it decreases again. This is called
post-tetanic stimulation.
6 This is not the case in the beginning, there was no high frequency stimulation. Therefore the
release probability here goes back to 0.5.
Post-tetanic stimulation: the increase in release probability takes a few ms.
LTP: the increase in release probability takes at least a few minutes. If you want to store the
information and compare the input with the stored information, you need this briefly higher release
probability.
2