Psychology Revision
Memory
Coding
- The way in which memory is stored in the memory
- Baddeley- gave 4 groups, 4 different types of words (acoustically similar, acoustically
dissimilar, semantically similar, semantically dissimilar). After STM recall, he found
acoustically similar words recall the worst. After LTM recall, he found semantically
similar words recall the worst.
Evaluations
- Artificial stimuli- Baddeley’s task wasn’t meaningful to the participant or very similar
to real life. It struggles to be generalised.
Capacity
- This refers to how much information can be held in the memory
- Jacobs (1887)- tried to measure digit span. He said 4 digits and asked a participant to
recall. If successful, another digit would be added to the sequence. The mean span
for digits was 9.3 and letters was 7.3.
- Miller (1956)- suggested things come in groups of 7 so STM must also come at a
capacity of 7 ‘plus or minus’ 2. He says recall is done by chunking (grouping sets of
digits or letters into sets of units or chunks).
Evaluations
- Lacking Validity- Jacob’s Study was done a long time ago and lacks control
- Over Chunking- Cowan (2001) suggests Miller overestimated STM capacity and
suggests its only around 4 chunks whilst Miller suggests 5 chunks.
Duration
- How long information can be kept in the memory
- STM Duration- Margaret and Lloyd Peterson (1959) gave 24 participants a 3 digit
consonant syllable (e.g. YCG) and a 3 digit number. The participant was asked to
count down from the 3 digit number (for different amounts of time 3-18 secs) and
then recall the letters. They found as the time of counting increased, their recall
ability decreased.
- LTM Duration- Bahrick and colleagues (1975) got 392 participants from Ohio to recall
people that attended their high school and recognise their yearbook photos
(participants were aged 17-74). After 15 years, recall was around 90% and after 48
years 70%. As for recognition, after 15 years 60% accurate, after 48 years 30%.
Shows LTM duration quite large.
Evaluations
- Artificial Stimuli- Peterson and Peterson’s stimuli was artificial. Study lacks external
validity.
, - Higher Validity- Bahrick’s study has higher external validity as the task was
meaningful and to do with real-life
Memory Stores
- Short-term Memory- the temporary memory store. This store has limited capacity.
The way in which things are coded is mainly acoustically (by sound). It is suggested
that its capacity is between 5 and 9 items. The amount of time a memory is kept in
this store (the duration) is between 18 and 30 seconds.
- Long-term Memory- memories in this store are suggested to be permanent. The way
in which things are coded is mainly semantically (by meaning), the capacity is
suggested to be unlimited. The duration is suggested to be a life time.
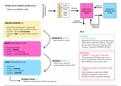
Multi-store Model
- This is a model that suggests how memory is stored, how a memory is moved from
one store to another, how something is remembered and the way in which it can be
forgotten. The model suggests that there are three stores: sensory register, short-
term memory and long-term memory
- Sensory Register- this stores information collected through the five senses but 2 in
particular are stored in certain areas : vision (iconic store) and hearing (echoic store).
In the iconic sensory store, information is retrieved visually. In the echoic sensory
store, information is retrieved acoustically. The capacity is vast as there are millions
of receptors but the information only lasts for around less than a second.
Sensory Register Retrieval
Short-term Long-term
Memory Memory
Iconic + Echoic
Rehearsal
Evaluations
- Research support- Baddeley’s research into coding supports the idea that LTM and
STM are independent and different.
- Multiple STM- the research in amnesia patient KF suggests that there are multiple
types of STM, however the Multi-store model suggests there is only one. KF could
remember some things short term but not others.
- Multiple Rehearsal- this study suggests there is one form of rehearsal. Craik and
Watson (1973) suggests that maintenance rehearsal only sustains storage in STM.
Elaborative rehearsal is needed for LTM storage.
Types of Long-term Memory- Tulving
- Episodic Memory- includes information about personal events. It is a long-term
memory store. It stores information about the time of the event and the people,
objects, places and behaviours involved in the event. Retrieval is only possible
consciously and with effort.
Memory
Coding
- The way in which memory is stored in the memory
- Baddeley- gave 4 groups, 4 different types of words (acoustically similar, acoustically
dissimilar, semantically similar, semantically dissimilar). After STM recall, he found
acoustically similar words recall the worst. After LTM recall, he found semantically
similar words recall the worst.
Evaluations
- Artificial stimuli- Baddeley’s task wasn’t meaningful to the participant or very similar
to real life. It struggles to be generalised.
Capacity
- This refers to how much information can be held in the memory
- Jacobs (1887)- tried to measure digit span. He said 4 digits and asked a participant to
recall. If successful, another digit would be added to the sequence. The mean span
for digits was 9.3 and letters was 7.3.
- Miller (1956)- suggested things come in groups of 7 so STM must also come at a
capacity of 7 ‘plus or minus’ 2. He says recall is done by chunking (grouping sets of
digits or letters into sets of units or chunks).
Evaluations
- Lacking Validity- Jacob’s Study was done a long time ago and lacks control
- Over Chunking- Cowan (2001) suggests Miller overestimated STM capacity and
suggests its only around 4 chunks whilst Miller suggests 5 chunks.
Duration
- How long information can be kept in the memory
- STM Duration- Margaret and Lloyd Peterson (1959) gave 24 participants a 3 digit
consonant syllable (e.g. YCG) and a 3 digit number. The participant was asked to
count down from the 3 digit number (for different amounts of time 3-18 secs) and
then recall the letters. They found as the time of counting increased, their recall
ability decreased.
- LTM Duration- Bahrick and colleagues (1975) got 392 participants from Ohio to recall
people that attended their high school and recognise their yearbook photos
(participants were aged 17-74). After 15 years, recall was around 90% and after 48
years 70%. As for recognition, after 15 years 60% accurate, after 48 years 30%.
Shows LTM duration quite large.
Evaluations
- Artificial Stimuli- Peterson and Peterson’s stimuli was artificial. Study lacks external
validity.
, - Higher Validity- Bahrick’s study has higher external validity as the task was
meaningful and to do with real-life
Memory Stores
- Short-term Memory- the temporary memory store. This store has limited capacity.
The way in which things are coded is mainly acoustically (by sound). It is suggested
that its capacity is between 5 and 9 items. The amount of time a memory is kept in
this store (the duration) is between 18 and 30 seconds.
- Long-term Memory- memories in this store are suggested to be permanent. The way
in which things are coded is mainly semantically (by meaning), the capacity is
suggested to be unlimited. The duration is suggested to be a life time.
Multi-store Model
- This is a model that suggests how memory is stored, how a memory is moved from
one store to another, how something is remembered and the way in which it can be
forgotten. The model suggests that there are three stores: sensory register, short-
term memory and long-term memory
- Sensory Register- this stores information collected through the five senses but 2 in
particular are stored in certain areas : vision (iconic store) and hearing (echoic store).
In the iconic sensory store, information is retrieved visually. In the echoic sensory
store, information is retrieved acoustically. The capacity is vast as there are millions
of receptors but the information only lasts for around less than a second.
Sensory Register Retrieval
Short-term Long-term
Memory Memory
Iconic + Echoic
Rehearsal
Evaluations
- Research support- Baddeley’s research into coding supports the idea that LTM and
STM are independent and different.
- Multiple STM- the research in amnesia patient KF suggests that there are multiple
types of STM, however the Multi-store model suggests there is only one. KF could
remember some things short term but not others.
- Multiple Rehearsal- this study suggests there is one form of rehearsal. Craik and
Watson (1973) suggests that maintenance rehearsal only sustains storage in STM.
Elaborative rehearsal is needed for LTM storage.
Types of Long-term Memory- Tulving
- Episodic Memory- includes information about personal events. It is a long-term
memory store. It stores information about the time of the event and the people,
objects, places and behaviours involved in the event. Retrieval is only possible
consciously and with effort.