Puberty starts as hypothalamus stimulates hypophysis (pituitary) to release gonadotropins which
stimulate the gonads to initiate puberty
Males Females
Primary sex organs (site of Testes (Cells of Sertoli in Ovaries
meiosis) seminiferous tubules in lobules)
Germinal epithelium
Gamete formation Sperm via spermatogenesis (for Ova via oogenesis (born with all
(gametogenesis) entire life after puberty) eggs stops at menopause)
Gametes Small and motile, many Large, immotile, 1 monthly
produced daily
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Stimulates sperm maturation Primary follicle → Graafian
Hormone) (72 days) follicle
LH (Luteinizing hormone) Stimulates Cells of Leydig to Ovulation (~day 14)+ formation
produce testosterone → of corpus luteum
spermatogenesis
Secondary sexual characteristics Deepening of voice, increases Widening of hips, breast
facial and body hair, enlarged development, menstruation
penis/testis
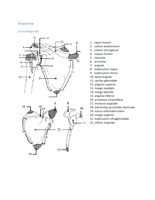
Males Function
Testis (primary sex organ) Spermatogenesis, release testosterone
Epididymis Stores sperm for maturation
Vas Deferens Transports sperm
Urethra Transports urine and sperm to exterior
Seminal vesicle Secrete fluid which is a food source for sperm
Prostate gland Secrete fluid to neutralise vaginal acidity
Cowper's glands (preejaculatory fluid) Secrete fluid for motility and viscosity, lubrication
Penis Deposit semen near cervix inside female
Sperm (haploid) Carry hereditary information from father to fuze with egg in
fertilization (Mitochondria found in middle piece in sperm)