Physiology notes
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Located outside of the skull and spine
Serves to bring information into the CNS and carry signals out of the
CNS
Peripheral Nervous System
o Somatic nervous system
Transmits signals to and from the central nervous
system
Afferent nerves (sensory)
Efferent nerves (motor)
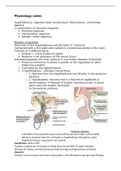
o Autonomic nervous system
Controls function of organs and glans
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves
Sympathetic = flight fight response
Parasympathetic = restores body to a state of
calm
Both afferent and efferent nerves
Efferent: Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves
o Sympathetic = flight fight response
o Parasympathetic = restores body to a state
of calm
Enteric nervous system in digestive tract.
Autonomic nervous system
- Innervates systems that cannot be controlled by the conscious brain
(heart, smooth muscle, blood vessels, most visceral organs, all
endocrine glands)
- Nervous parasympathetic and sympathetic system
- Sympathetic = increased heart rate (catabolic processes)
- Parasympathetic = vasodilation, energy substrates stored in
glycogen, fat and muscle (anabolic processes)
Sympathetic Parasympathetic
Originates in spinal cord Originates in brain stem
Dilates pupils Constricts pupils
Stops secretion of saliva Saliva production
Dilates bronchioles Constrict bronchioles
- Antagonistic neurons control heart rate: some speed it up, others
slow it down
- Parasympathetic via nervus vagus and only on frequency
(pacemaker), sympathetic via cardiac nerve and influences
frequency + contraction.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Located outside of the skull and spine
Serves to bring information into the CNS and carry signals out of the
CNS
Peripheral Nervous System
o Somatic nervous system
Transmits signals to and from the central nervous
system
Afferent nerves (sensory)
Efferent nerves (motor)
o Autonomic nervous system
Controls function of organs and glans
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves
Sympathetic = flight fight response
Parasympathetic = restores body to a state of
calm
Both afferent and efferent nerves
Efferent: Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves
o Sympathetic = flight fight response
o Parasympathetic = restores body to a state
of calm
Enteric nervous system in digestive tract.
Autonomic nervous system
- Innervates systems that cannot be controlled by the conscious brain
(heart, smooth muscle, blood vessels, most visceral organs, all
endocrine glands)
- Nervous parasympathetic and sympathetic system
- Sympathetic = increased heart rate (catabolic processes)
- Parasympathetic = vasodilation, energy substrates stored in
glycogen, fat and muscle (anabolic processes)
Sympathetic Parasympathetic
Originates in spinal cord Originates in brain stem
Dilates pupils Constricts pupils
Stops secretion of saliva Saliva production
Dilates bronchioles Constrict bronchioles
- Antagonistic neurons control heart rate: some speed it up, others
slow it down
- Parasympathetic via nervus vagus and only on frequency
(pacemaker), sympathetic via cardiac nerve and influences
frequency + contraction.