Lecture 2(a)
Account 1 and 2
Circuit of economic transactions:
- Economic subjects → households, business enterprises, government and the rest of
the world
- Economic objects: goods and services produced in the economy.
- Processes: production, saving, investment, consumption, taxation, government
expenditure and imports and exports.
- Production factors → labour, capital, entrepreneurship, and natural resources
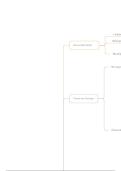
Flow of income → T → taxes
Flow of good and services (G&S) → G → government spending
RoW = Rest of the World X → exports Z → imports
PF = production factors Z → imports
I → investment C → consumption
RoW
Z X
Market
for PF
G T
T Government T
Business Individuals and
Enterprises Households
Financial institutions
I S
G T
C
Market
for G&S
Z X
RoW
NOTE! Taxes always flow towards government
Government spending always flows away from government
Pink line = financial stream → compensation received
Notes can only be purchased through the following details:
or 0829369077 1
, - I&H → labour flows to Market for PF → used by BE in production process →
transform PF into G&S → G&S sold to I&H → follows the blue line
o G&S are bought by I&H → the money is paid to BE → BE use these funds to
pay I&H for their PF given to them → follows the pink line
- Pink line + blue line = two sector macro model → streams should be relatively
equal
o If more in financial stream than goods and services to be bought → causes
inflationary drive (drives prices up)
- Government → either charge tax or provide through spending → households and
business are taxed directly
- Financial institutes → facilitate financial flow → they put money into circulation
- RoW → exports and imports of PF and G&S
Economic circuit as a conceptual basis for the National Accounts:
- National accounts → based on the principle of double entry → for every debit
entry there is a corresponding credit entry.
o Built on the basic structural macroeconomic equation → describes the
interaction of all the economic subjects involved in the economy
▪ Y = C + I + G + (X − Z)
o Closed-circuit model (circuit excluding RoW) → highlights identity in
national accounting
▪ Total expenditure (by enterprises) = total income (received by
households)
- Economic subjects → have certain unique characteristics, capabilities, motives,
principles and abilities
- Primary objective of national accounts → summation of the value of production
of final G&S by each individual producer in the economy in order to obtain the
total value (aggregate) of national production (in monetary terms)
- Production of goods → linked to purchase of raw materials and factor services by
enterprises
o Purchases provide the link between total expenditure and production
- Total production of final G&S → purchased by households (final consumption
expenditure by households), business enterprises (gross fixed capital formation),
government (final consumption expenditure by general government) and the
foreign sector (net export expenditure)
o Therefore, total expenditure (TE) on goods and services is equal to the total
value of production (TP)
▪ 𝑇𝐸 ≡ 𝑇𝑃
- All income derived from production of final G&S equals total income (e.g. salaries
and wages, interest, rent, and profits).
o Therefore, total revenue (TR) earned from production is equal to the value
of total production (TP).
▪ 𝑇𝑅 ≡ 𝑇𝑃
NOTE! Identities (≡)vs equations (=)
Identities → statement derived directly from definitions or arithmetic ratios → therefore it
is always true
- any value(s) of the unknown variable(s) will satisfy an identity → 𝑎2 = 𝑎 × 𝑎 (any
value used in place of 𝑎 will satisfy the identity)
Equation → satisfied by a unique value or set of values
- specific values of an unknown variable will satisfy an equation → 𝑎2 = 4 (only ± 2
will satisfy the equation)
Notes can only be purchased through the following details:
or 0829369077 2
Account 1 and 2
Circuit of economic transactions:
- Economic subjects → households, business enterprises, government and the rest of
the world
- Economic objects: goods and services produced in the economy.
- Processes: production, saving, investment, consumption, taxation, government
expenditure and imports and exports.
- Production factors → labour, capital, entrepreneurship, and natural resources
Flow of income → T → taxes
Flow of good and services (G&S) → G → government spending
RoW = Rest of the World X → exports Z → imports
PF = production factors Z → imports
I → investment C → consumption
RoW
Z X
Market
for PF
G T
T Government T
Business Individuals and
Enterprises Households
Financial institutions
I S
G T
C
Market
for G&S
Z X
RoW
NOTE! Taxes always flow towards government
Government spending always flows away from government
Pink line = financial stream → compensation received
Notes can only be purchased through the following details:
or 0829369077 1
, - I&H → labour flows to Market for PF → used by BE in production process →
transform PF into G&S → G&S sold to I&H → follows the blue line
o G&S are bought by I&H → the money is paid to BE → BE use these funds to
pay I&H for their PF given to them → follows the pink line
- Pink line + blue line = two sector macro model → streams should be relatively
equal
o If more in financial stream than goods and services to be bought → causes
inflationary drive (drives prices up)
- Government → either charge tax or provide through spending → households and
business are taxed directly
- Financial institutes → facilitate financial flow → they put money into circulation
- RoW → exports and imports of PF and G&S
Economic circuit as a conceptual basis for the National Accounts:
- National accounts → based on the principle of double entry → for every debit
entry there is a corresponding credit entry.
o Built on the basic structural macroeconomic equation → describes the
interaction of all the economic subjects involved in the economy
▪ Y = C + I + G + (X − Z)
o Closed-circuit model (circuit excluding RoW) → highlights identity in
national accounting
▪ Total expenditure (by enterprises) = total income (received by
households)
- Economic subjects → have certain unique characteristics, capabilities, motives,
principles and abilities
- Primary objective of national accounts → summation of the value of production
of final G&S by each individual producer in the economy in order to obtain the
total value (aggregate) of national production (in monetary terms)
- Production of goods → linked to purchase of raw materials and factor services by
enterprises
o Purchases provide the link between total expenditure and production
- Total production of final G&S → purchased by households (final consumption
expenditure by households), business enterprises (gross fixed capital formation),
government (final consumption expenditure by general government) and the
foreign sector (net export expenditure)
o Therefore, total expenditure (TE) on goods and services is equal to the total
value of production (TP)
▪ 𝑇𝐸 ≡ 𝑇𝑃
- All income derived from production of final G&S equals total income (e.g. salaries
and wages, interest, rent, and profits).
o Therefore, total revenue (TR) earned from production is equal to the value
of total production (TP).
▪ 𝑇𝑅 ≡ 𝑇𝑃
NOTE! Identities (≡)vs equations (=)
Identities → statement derived directly from definitions or arithmetic ratios → therefore it
is always true
- any value(s) of the unknown variable(s) will satisfy an identity → 𝑎2 = 𝑎 × 𝑎 (any
value used in place of 𝑎 will satisfy the identity)
Equation → satisfied by a unique value or set of values
- specific values of an unknown variable will satisfy an equation → 𝑎2 = 4 (only ± 2
will satisfy the equation)
Notes can only be purchased through the following details:
or 0829369077 2