Muscle metabolism and sport
1. Oxygen
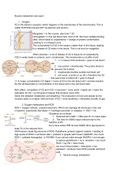
O2 is the electron acceptor, which happens in the membranes of the mitochondria. This is
called OXPHOS (harvest ATP via electron and proton).
Myoglobin = in the muscle, also bind 1 O2
Hemoglobin= in the red blood cells, bind 4 O2. We have multiple binding
sites, which leads to cooperativity > change of protein conformation.
Leading to a s-shaped curve.
The concentration of O2 in the lungs is higher than in the tissue, leading
to a release of O2 when in the tissue. This is not true for myoglobin.
When exercise > a lot of release of O2 in tissue bc of cooperativity.
CO2 in water leads to carbonic acid > bicarbonate. This bicarbonate is a buffer of pH.
1. >> in tissue CO2 produced > goes to red blood
cell
2. loss proton > bicarbonate. The proton binds to
Hb (prevent O2 to bind)
3. bicarbonate shuttles outside red blood cell
4. net result: a proton is on Hb > therefore the O2
that was binds is kicked off > goes to tissue!
>> In lungs: concentration O2 higher > move of O2 to the red blood cell > reverse reaction
So this all depended on concentration in the tissue and in the red blood cells.
Bohr effect: competition of O2 and CO2. in exercise > more acids > higher pH > lower the
saturation for O2 > so O2 goes to tissues that produce more CO2.
Direct link between metabolism and breathing: The production of CO2 and lactate by the
muscles leads to a higher HHb and lack of O2 > more breathing > stimulates transfer of gas.
2. Oxygen metabolism and ROS
ROS = oxygen radicals, unpaired electrons. Which can damage all structures in the cell.
2 systems: superoxide dismutase >> hydrogen peroxide. or catalase >> H2O + O2.
Glutathion as co-factor
1. Reduced form GSH + HSG puts H+ to make water
2. The new for GSSG stays reduced due to the
NADPH of PP
Ery’s have active PPP & have NADH (from glycolysis) to
keep Fe in the reduced form.
FAVA beans create big amounts of ROS. Glutathione protects against malaria > leading to
high levels of ROS in red blood cells > problem in people with Favism (G6DHP). Too much
ROS > oxidized hemoglobin. In FAVISM: If you cannot make enough NADPH > not enough
to reduce glutathione > no e- donation > too much
ROS > oxy Hb > heinz body
too much heinz bodies > hemolysis > iron
released > produce more ROS (outside red blood
cell).
3. Muscle energy metabolism
1. Oxygen
O2 is the electron acceptor, which happens in the membranes of the mitochondria. This is
called OXPHOS (harvest ATP via electron and proton).
Myoglobin = in the muscle, also bind 1 O2
Hemoglobin= in the red blood cells, bind 4 O2. We have multiple binding
sites, which leads to cooperativity > change of protein conformation.
Leading to a s-shaped curve.
The concentration of O2 in the lungs is higher than in the tissue, leading
to a release of O2 when in the tissue. This is not true for myoglobin.
When exercise > a lot of release of O2 in tissue bc of cooperativity.
CO2 in water leads to carbonic acid > bicarbonate. This bicarbonate is a buffer of pH.
1. >> in tissue CO2 produced > goes to red blood
cell
2. loss proton > bicarbonate. The proton binds to
Hb (prevent O2 to bind)
3. bicarbonate shuttles outside red blood cell
4. net result: a proton is on Hb > therefore the O2
that was binds is kicked off > goes to tissue!
>> In lungs: concentration O2 higher > move of O2 to the red blood cell > reverse reaction
So this all depended on concentration in the tissue and in the red blood cells.
Bohr effect: competition of O2 and CO2. in exercise > more acids > higher pH > lower the
saturation for O2 > so O2 goes to tissues that produce more CO2.
Direct link between metabolism and breathing: The production of CO2 and lactate by the
muscles leads to a higher HHb and lack of O2 > more breathing > stimulates transfer of gas.
2. Oxygen metabolism and ROS
ROS = oxygen radicals, unpaired electrons. Which can damage all structures in the cell.
2 systems: superoxide dismutase >> hydrogen peroxide. or catalase >> H2O + O2.
Glutathion as co-factor
1. Reduced form GSH + HSG puts H+ to make water
2. The new for GSSG stays reduced due to the
NADPH of PP
Ery’s have active PPP & have NADH (from glycolysis) to
keep Fe in the reduced form.
FAVA beans create big amounts of ROS. Glutathione protects against malaria > leading to
high levels of ROS in red blood cells > problem in people with Favism (G6DHP). Too much
ROS > oxidized hemoglobin. In FAVISM: If you cannot make enough NADPH > not enough
to reduce glutathione > no e- donation > too much
ROS > oxy Hb > heinz body
too much heinz bodies > hemolysis > iron
released > produce more ROS (outside red blood
cell).
3. Muscle energy metabolism