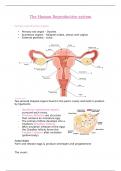
, Section One Section Two
Definition of Anatomy
Subdisciplines
Anatomical Position
Common Anatomical Terms
TERMS OF RELATIONSHIP
BODY CAVITIES
Anatomical Planes
The skin: Burns, Langer Lines
Types of Fascia
Types of Muscle
The Skeleton: Types of Bones
Anatomy
Anatomy is the study of body
structures, their organization and
location . Ana-tomy literally means “to
cut”.
Subdisciplines of anatomy
Systemic anatomy Surface anatomy Clinical anatomy Regional anatomy
Studying how various Superficial/visual/ The practical Studying organs and
organs & structures topographic anatomy. application of structures in a
work together to Study of the external anatomy to diagnosis specific region/area.
perform a function. body at rest or in and treatment of.
action with aim of Incorporates systemic E.g. The Abdomen.
E.g. The Respiratory visualizing landmarks & regional anatomy.
System: mouth, nose, of structures that lie
windpipes, lungs. beneath the skin. E.g. Carpal Tunnel Sx.
,Introduction
Directional References
Medial
Closer to the midline
Lateral
Further from the midline
Superior
Upwards. Closer to the head
Inferior
Downward. Closer to the feet
Anatomical POSN Dorsal Ventral
Standing upright Behind. Posterior. Infront.
Head, eyes facing forward (Dererie = Bum) Anterior-Ventral (Air-Vent)
Upper limbs at the side
Palms faced forward
Feet pointing forward
Forward=anterior
Distal Proximal
Further from pt of attachment Closer to pt of attachment
ANATOMICAL PLANES
MEDIAL PLANE CORONAL PLANE transverse Plane
VERTICAL (upright) VERTICAL plane Horizontal plane
Passes through CENTRE Perpendicular to medial plane Divides superior and inferior.
Divides body 2 equal halves. Divides anterior and posterior. Top & Bottom
Left and right. Front and back.
,Planes of movement at joint Common Anatomical Terms
Common Anatomical
Ear Aural
Navel Umbulicus
Thumb Pollex
Fingers Digital
Arm Brachial
Forearm Ante-brachial
Buttock Gluteal
Ribs Thoracic
Thigh Femoral
Armpit Axillary
Sole Plantar
Head Cranial
Mouth Oral
Nose Nasal
Cheek Buccal
Jaw Mandible
Neck Cervical
7 Body Cavities
, Skin
Layers Lines
Langer lines/ cleavage lines
A superficial layer.
Able to regenerate
Natural orientation of collagen
It is avascular, few nerve endings. fibres in the dermis.
Runs parallel to muscle fibres
Clinically significant: if surgeons
Dense layer made of collagen and elastin. make linear incisions along these
Contains hair follicles, glands, muscles. lines, healing is faster.
Has a blood supply and nerve endings.
Tension Lines
Linear opening made along a
Loose connective tissue and fat. langer line and extrapolated due
Contains sweat glands, lymph and blood vessels.
to a pin being driven into skin.
Burns
Healing
Few days
21 days
Needs
grafting
Muscle
FASCIA
Fascia is a band of connective tissue,
primarily collagen, beneath the skin
that attaches, stabilizes, encloses, and
separates & and other internal organs.
Deep Fascia
Dense, organized connective tissue.
Devoid of fat.
Investing fascia
Extends from inner layer of deep
fascia between individual muscles
and neurovascular bundles.
Intermuscular septa
Extends from inner deep fascia to
bone to form compartments/
sleeves around muscles, nerves and
blood supply.