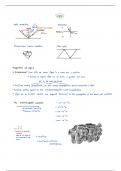
CURRENT DIVIDER RULE
• Only in case of Parallel connected circuit
VOLTAGE DIVIDER RULE
• Only in case of Series connected circuit
KIRCHHOFF’S LAWS
# Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
, • The total current leaving a junction is equal to the total current entering
that junction.
I= I1 + I2 + I3 + I4
# Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)
• The algebraic sum of the products of currents and resistances in each of the
conductors in any closed path (or mesh) in a network plus the algebraic
sum of the e.m.fs. in that path is zero.
1) Battery emf Sign Conventions in KVL
→ A rise in voltage should be given a + ve sign and a fall in voltage a −ve sign.
→ As we go from the −ve terminal of a battery to its +ve terminal, there is a
rise in potential, hence this voltage should be given a + ve sign.
→ If, on the other hand, we go from +ve terminal to −ve terminal, then there
is a fall in potential.
→ It is important to note that the sign of the battery e.m.f. is independent of
the direction of the current through that branch.