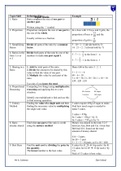
The need for a peaceful death
Care of the dying patient
Special skill is required on the part of the nurse
Nursing care usually involves alleviation of pain and discomfort and the provision of
personal support to the patient and to those close to him/her
Known as palliative care: an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and
their families facing the problems associated with life threatening illness through the
prevention and relief of suffering
The process of dying
Dying is a complex process both physically and mentally
Physical level
Loss of muscle tone and wasting of muscle
Reduction in peristalsis
Slowing down of blood circulation
Decreased appetite and fluid intake
The presence of pain and discomfort
Changes in sensory perception
Weakness and fatigue
Possible changes in awareness or levels or consciousness
Psychological level
Becoming aware
Becoming aware that the/she is dying is brought about by being told or by own
realisation. This stage is preceded by anxiety or premonition. Shock accompanies this
phase together with feeling of unreality, panic and prolonged anxiety
Nursing care
Sincere empathy is essential. Give encouragement and assure the patient of support
Convince the patient and family (through attitude0 that they are accepted and are
free to express their feelings
Ensure privacy, encourage venting of emotions and be warm and accepting
Be available when the person has a desire to speak to you
Denial
The patient tries to escape the reality and cannot accept the seriousness of the illness
Nursing care
Accept that the patient/family is not ready to accept the seriousness of the illness
but do not encourage denial
Give the family the opportunity to stay together to reassure each other
Do not admire the denial as bravery
Spend time with the patient and family
If possible, allow the patient to go home to perform rituals if they wish
Care of the dying patient
Special skill is required on the part of the nurse
Nursing care usually involves alleviation of pain and discomfort and the provision of
personal support to the patient and to those close to him/her
Known as palliative care: an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and
their families facing the problems associated with life threatening illness through the
prevention and relief of suffering
The process of dying
Dying is a complex process both physically and mentally
Physical level
Loss of muscle tone and wasting of muscle
Reduction in peristalsis
Slowing down of blood circulation
Decreased appetite and fluid intake
The presence of pain and discomfort
Changes in sensory perception
Weakness and fatigue
Possible changes in awareness or levels or consciousness
Psychological level
Becoming aware
Becoming aware that the/she is dying is brought about by being told or by own
realisation. This stage is preceded by anxiety or premonition. Shock accompanies this
phase together with feeling of unreality, panic and prolonged anxiety
Nursing care
Sincere empathy is essential. Give encouragement and assure the patient of support
Convince the patient and family (through attitude0 that they are accepted and are
free to express their feelings
Ensure privacy, encourage venting of emotions and be warm and accepting
Be available when the person has a desire to speak to you
Denial
The patient tries to escape the reality and cannot accept the seriousness of the illness
Nursing care
Accept that the patient/family is not ready to accept the seriousness of the illness
but do not encourage denial
Give the family the opportunity to stay together to reassure each other
Do not admire the denial as bravery
Spend time with the patient and family
If possible, allow the patient to go home to perform rituals if they wish