Eukaryotes
Chapter 3
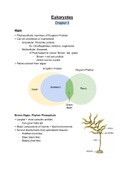
Algae
= Photosynthetic members of Kingdom Protista
= Can be unicellular or multicellular
- Unicellular: Plant-like protists
- Ex: Dinoflagellates, diatoms, euglenoids
- Multicellular: Seaweed
- 3 Phyla based on colour: Brown, red, green
- Brown + red are protists
- Green can be a plant
= Plants evolved from algae
Brown Algae: Phylum Phaeophyta
= Largest + most complex protists
- Can grow hella tall
= Major components of marine + tidal environments
= No true leaves/roots (has specialized tissues)
- Holdfast (root like)
- Stipe (stem like)
- Blades (leaf like)
,Red Algae: Phylum Rhodophyta
= Abundant in coastal waters of tropical oceans
= Shorter than brown algae
= Has green chlorophyll
- + Additional pigment called phycoerythrin
- Sensitive to light waves that reach greater ocean depths
- Can thrive in deeper ocean depths
- Reflects red wavelengths of light thus why they’re red-coloured
Green Algae: Phylum Chlorophyta
= Most are aquatic
- Common in freshwater; can be in saltwater
= Varied ecosystems
- Ex: In sea ice, on trees, sloth furs
Similarity to plants
= Same chlorophyll type
= Same colour (green)
= Cellulose cell walls
= Stores food reserves in form of starch
- Bacteria, fungi, animals store food as glycogen
= Similar DNA sequences
From Algae to Plants
Adaptation to Life on Land
= Protection from desiccation (drying out)
, = System to transport water + dissolved substances from outside environment into
body cells
= System to support body of the plant
- Lifting it up to the light + air
= Slow af process
= Earliest plants started out in moist environments
- Transferred water + dissolved substances via osmosis + diffusion
- Limited their max height aka these plants hella short
Plant Embryos
= Plants reproduce via embryos (organism’s early pre-birth stage)
- Small, multicellular plants dependent on parent plant (for some time)
= Recent developments in plant evolution are: (Order of who came first)
- Vascular tissue
- Used to transport materials
- Seeds
- Protect + nourish the embryo
- Flowers
Vascular Tissue, Leaves, Roots
= First land plants didn’t have tissues that allowed for the transport of diff materials
over long distances
- Song vascular tissues evolved
- Vascular plants
= Vascular plants had 2 types of vascular tissue (transports materials)
- Xylem
- Carries water + minerals from roots to the top
- Has dead tube-shaped cells that has tough material called lignin
- Lignified xylem forms firm structure that allows w + m to
be transported
- Xylem + lignin allowed plants to grow taller
- Phloem
- Made of living cells arranged in tubular form
- Used for transporting larger molecules (ex: sugars)
= Vas tissue allowed evolution of roots
- Strong anchoring ability
- Cells specialized in absorbing & transporting w + m
Chapter 3
Algae
= Photosynthetic members of Kingdom Protista
= Can be unicellular or multicellular
- Unicellular: Plant-like protists
- Ex: Dinoflagellates, diatoms, euglenoids
- Multicellular: Seaweed
- 3 Phyla based on colour: Brown, red, green
- Brown + red are protists
- Green can be a plant
= Plants evolved from algae
Brown Algae: Phylum Phaeophyta
= Largest + most complex protists
- Can grow hella tall
= Major components of marine + tidal environments
= No true leaves/roots (has specialized tissues)
- Holdfast (root like)
- Stipe (stem like)
- Blades (leaf like)
,Red Algae: Phylum Rhodophyta
= Abundant in coastal waters of tropical oceans
= Shorter than brown algae
= Has green chlorophyll
- + Additional pigment called phycoerythrin
- Sensitive to light waves that reach greater ocean depths
- Can thrive in deeper ocean depths
- Reflects red wavelengths of light thus why they’re red-coloured
Green Algae: Phylum Chlorophyta
= Most are aquatic
- Common in freshwater; can be in saltwater
= Varied ecosystems
- Ex: In sea ice, on trees, sloth furs
Similarity to plants
= Same chlorophyll type
= Same colour (green)
= Cellulose cell walls
= Stores food reserves in form of starch
- Bacteria, fungi, animals store food as glycogen
= Similar DNA sequences
From Algae to Plants
Adaptation to Life on Land
= Protection from desiccation (drying out)
, = System to transport water + dissolved substances from outside environment into
body cells
= System to support body of the plant
- Lifting it up to the light + air
= Slow af process
= Earliest plants started out in moist environments
- Transferred water + dissolved substances via osmosis + diffusion
- Limited their max height aka these plants hella short
Plant Embryos
= Plants reproduce via embryos (organism’s early pre-birth stage)
- Small, multicellular plants dependent on parent plant (for some time)
= Recent developments in plant evolution are: (Order of who came first)
- Vascular tissue
- Used to transport materials
- Seeds
- Protect + nourish the embryo
- Flowers
Vascular Tissue, Leaves, Roots
= First land plants didn’t have tissues that allowed for the transport of diff materials
over long distances
- Song vascular tissues evolved
- Vascular plants
= Vascular plants had 2 types of vascular tissue (transports materials)
- Xylem
- Carries water + minerals from roots to the top
- Has dead tube-shaped cells that has tough material called lignin
- Lignified xylem forms firm structure that allows w + m to
be transported
- Xylem + lignin allowed plants to grow taller
- Phloem
- Made of living cells arranged in tubular form
- Used for transporting larger molecules (ex: sugars)
= Vas tissue allowed evolution of roots
- Strong anchoring ability
- Cells specialized in absorbing & transporting w + m