Decision-making skills = ability of managers to make better decisions than their competitors, make the decisions faster
than competitors & implement decisions effectively & efficiently
Decision = Implies managers faced with threat, problem or opportunity
Decisions in 4 fundamental management function:
Planning = decisions about goals & when & where they will be realised
Controlling = notice goals not realised
Organising = decisions involving creation of org structure & deployment of resources enabling org to attain its
goals
Leading = decide how to influence & direct behaviour of subordinates so they will work willingly to pursue goals of
org
5.2 Relationship between problems, problem-solving & decision-making:
Problem = Whenever managers perceive a difference between what happened & what they planned to happen
Problem-solving = Process of taking corrective action that will solve a problem
Decision-making = process of selecting an alternative course of action that will solve a problem
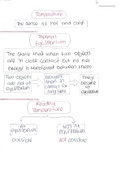
5.3 Types of managerial decisions:
Programmed decisions:
Repetitive & routine
Have polices, standard operating procedures & rules
Ex: processing of payroll vouchers, processing of graduation candidates, processing admission of athletes to a
sport club, buying stationary or procuring raw materials
Non-programmed decisions:
Novel, unstructured & have not occurred before
Complex, elusive & no established method for dealing with them
Ex: org decide to merge with another for 1st time
1
, 5.4 Decision-making conditions:
CERTAINTY RISK UNCERTAINTY
Complete certainty Some certainty Complete uncertainty
Available options & Outcome of each Outcome of each
benefits or costs of each alternative is not known in alternative is un
are known advance predictable
No element of change Probability can be assigned Probability cannot be
intervenes between option to each alternative assigned to each
& its outcome outcome alternative outcome
Decision is a sure thing Decision is a gamble Decision requires guts
Programmed decisions Most difficult, complex,
Objective probability: novel circumstances
EXAMPLE based on historical
purchase of government evidence Non-programmed
treasury bill likelihood that particular
knowing income taxes are state of things will occur
due on 15 April based on hard facts &
figures
Subjective probability:
rely on personal estimate
& belief
FACTORS OF UNCERTAINTY & HIGH RISK
Economic recessions, stock market crashes, hostile takeovers
Physical industrial accidents, supply breakdowns, product failure
Personnel strikes, workplace violence
Criminal theft of money & goods, product tampering
Theft of info, tampering of company records, cyber attacks
Reputation rumour mongering, defamation
Natural disasters: fires, floods, earthquakes
5.5 Decision-making models:
Two primary decision-making models
1. Rational model {“optimising”}
= decision-maker selects the best possible solution to problem
2. Bounded-rationality model {“satisficing”}
= decision-maker selects 1st possible solution to problem
that meets the minimal criteria
SATISFICE (BOUNDED-RATIONAL MODEL)
Programmed low-risk or certain decisions
2