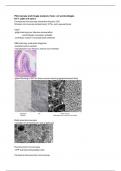
Conservatism: PRAGMATISM p270
TENET
-
Core value of conservatism – flexible
Informed by empiricism and have deep distrust of abstract theories favoured by political ideas such as liberalism and
socialism
- All changes derived from empiricism and the aim of making society more stable = later, one nation conservatism
pragmatically accepted and continued the radical changes made to British society by Attlee’s labour government. Such as
state intervention in the economy and the creation of the welfare state.
- Keep what’s working and new, get rid of traditions which don’t work. We adapt with empiricism. Tradition
has worked over time, therefore its kept until it proves not to work, then it is discarded. Dogmatic is bad
as they would be holding into things which don’t work. Don’t follow abstract ideas as the change of
getting it right is unlikely
- Defining feature as any split is a form of pragmatism
Key thinkers: Dichotomies Key terms:
- Burkes idea of ‘change to conserve’ influenced There are none. The
conservative PMs whole ideology is about Pragmatic - dealing with
- Peel’s ‘tanworth Manifesto’ 1834 argued conserving the same things sensibly and
things, therefore
conservatism was pragmatic not reactionary. Put into
different views of being realistically in a way that
practice in acceptance of great reform act 1832 –
middle class men had vote, pragmatic accepting social
pragmatic wouldn’t be is based on practical
conservative. If there is
emerging class of industrial revolution = integrated into change over the years
rather than theoretical
political system so that there are new considerations.
- Disraeli approached Artisan Dwellings act 1985 – dealt views, these modern
with slum clearance, in similar pragmatic fashion views are pragmatic –
Tradition – the
shows that everyone transmission of customs
believes it as the or beliefs from generation
change is pragmatic.
to generation, or the fact
New right – likes of being passed on in this
traditional ideas, more
fixed and ideological, way
less likely to adapt, Religion - the belief in
more dogmatic and
inflexible and worship of a
superhuman controlling
power, especially a
personal God or gods
TENET
-
Core value of conservatism – flexible
Informed by empiricism and have deep distrust of abstract theories favoured by political ideas such as liberalism and
socialism
- All changes derived from empiricism and the aim of making society more stable = later, one nation conservatism
pragmatically accepted and continued the radical changes made to British society by Attlee’s labour government. Such as
state intervention in the economy and the creation of the welfare state.
- Keep what’s working and new, get rid of traditions which don’t work. We adapt with empiricism. Tradition
has worked over time, therefore its kept until it proves not to work, then it is discarded. Dogmatic is bad
as they would be holding into things which don’t work. Don’t follow abstract ideas as the change of
getting it right is unlikely
- Defining feature as any split is a form of pragmatism
Key thinkers: Dichotomies Key terms:
- Burkes idea of ‘change to conserve’ influenced There are none. The
conservative PMs whole ideology is about Pragmatic - dealing with
- Peel’s ‘tanworth Manifesto’ 1834 argued conserving the same things sensibly and
things, therefore
conservatism was pragmatic not reactionary. Put into
different views of being realistically in a way that
practice in acceptance of great reform act 1832 –
middle class men had vote, pragmatic accepting social
pragmatic wouldn’t be is based on practical
conservative. If there is
emerging class of industrial revolution = integrated into change over the years
rather than theoretical
political system so that there are new considerations.
- Disraeli approached Artisan Dwellings act 1985 – dealt views, these modern
with slum clearance, in similar pragmatic fashion views are pragmatic –
Tradition – the
shows that everyone transmission of customs
believes it as the or beliefs from generation
change is pragmatic.
to generation, or the fact
New right – likes of being passed on in this
traditional ideas, more
fixed and ideological, way
less likely to adapt, Religion - the belief in
more dogmatic and
inflexible and worship of a
superhuman controlling
power, especially a
personal God or gods