WGU D669 – Early Literacy Methods Objective Assessment | OA
Questions & Answers | 2026 Update | 100% Correct.
Domain 1: Foundations of Early Literacy
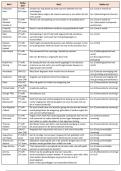
1. What is emergent literacy?
Answer: The skills, knowledge, and attitudes that precede formal reading and writing
development.
Rationale: Literacy development begins long before conventional reading instruction.
2. Which component of literacy focuses on understanding spoken
language sounds?
Answer: Phonological awareness
Rationale: It includes recognizing and manipulating sounds in words.
3. Why is oral language development critical in early literacy?
Answer: It forms the foundation for reading comprehension and vocabulary growth.
Rationale: Children must understand language before decoding written text.
4. Print awareness refers to:
Answer: Understanding how print works and recognizing written language.
Rationale: Includes concepts like reading left to right and recognizing letters.
5. Which environment best supports emergent literacy?
Answer: A print-rich environment with meaningful reading and writing experiences.
Rationale: Exposure encourages natural literacy development.
Domain 2: Phonological Awareness
6. Which skill develops first in phonological awareness?
,Answer: Word awareness
Rationale: Children recognize words before syllables and phonemes.
7. Identifying the first sound in a word demonstrates:
Answer: Phonemic awareness
Rationale: It involves working with individual phonemes.
8. Which activity best supports phonemic awareness?
Answer: Blending sounds to form words
Rationale: Blending strengthens decoding ability.
9. Rhyming is important because it:
Answer: Helps children hear sound patterns in words.
Rationale: It builds early sound discrimination skills.
10. Phonological awareness instruction should be:
Answer: Explicit and developmentally appropriate.
Rationale: Direct instruction improves literacy outcomes.
Domain 3: Phonics & Word Recognition
11. Phonics instruction teaches students to:
Answer: Connect letters with sounds.
Rationale: Phonics focuses on decoding written language.
12. What is decoding?
Answer: Translating written words into spoken language.
Rationale: Essential for word recognition.
,13. Which strategy supports phonics instruction?
Answer: Systematic and explicit instruction
Rationale: Structured approaches improve mastery.
14. Sight words are:
Answer: High-frequency words recognized automatically.
Rationale: Many cannot be decoded easily using phonics rules.
15. Word families help students:
Answer: Recognize patterns in spelling and sounds.
Rationale: Improves decoding efficiency.
Domain 4: Fluency
16. Reading fluency includes accuracy, rate, and:
Answer: Prosody
Rationale: Expression reflects comprehension.
17. Why is fluency important?
Answer: It allows readers to focus on meaning rather than decoding.
Rationale: Automaticity supports comprehension.
18. Which activity best builds fluency?
Answer: Repeated reading
Rationale: Repetition improves speed and accuracy.
19. Choral reading supports fluency by:
Answer: Reducing anxiety and modeling expression.
Rationale: Group reading builds confidence.
, 20. A fluent reader typically:
Answer: Reads smoothly with appropriate phrasing.
Rationale: Indicates strong decoding skills.
Domain 5: Vocabulary Development
21. Vocabulary instruction should be:
Answer: Intentional and contextualized.
Rationale: Students learn best through meaningful exposure.
22. Tier 2 words are:
Answer: High-utility academic vocabulary words.
Rationale: Common across content areas.
23. Which strategy best supports vocabulary growth?
Answer: Interactive read-alouds
Rationale: Introduces rich language in context.
24. Morphology instruction helps students:
Answer: Understand word meanings through roots and affixes.
Rationale: Supports decoding and comprehension.
25. Repeated exposure to words:
Answer: Strengthens vocabulary retention.
Rationale: Multiple encounters deepen understanding.
Domain 6: Reading Comprehension
26. Reading comprehension is best defined as:
Questions & Answers | 2026 Update | 100% Correct.
Domain 1: Foundations of Early Literacy
1. What is emergent literacy?
Answer: The skills, knowledge, and attitudes that precede formal reading and writing
development.
Rationale: Literacy development begins long before conventional reading instruction.
2. Which component of literacy focuses on understanding spoken
language sounds?
Answer: Phonological awareness
Rationale: It includes recognizing and manipulating sounds in words.
3. Why is oral language development critical in early literacy?
Answer: It forms the foundation for reading comprehension and vocabulary growth.
Rationale: Children must understand language before decoding written text.
4. Print awareness refers to:
Answer: Understanding how print works and recognizing written language.
Rationale: Includes concepts like reading left to right and recognizing letters.
5. Which environment best supports emergent literacy?
Answer: A print-rich environment with meaningful reading and writing experiences.
Rationale: Exposure encourages natural literacy development.
Domain 2: Phonological Awareness
6. Which skill develops first in phonological awareness?
,Answer: Word awareness
Rationale: Children recognize words before syllables and phonemes.
7. Identifying the first sound in a word demonstrates:
Answer: Phonemic awareness
Rationale: It involves working with individual phonemes.
8. Which activity best supports phonemic awareness?
Answer: Blending sounds to form words
Rationale: Blending strengthens decoding ability.
9. Rhyming is important because it:
Answer: Helps children hear sound patterns in words.
Rationale: It builds early sound discrimination skills.
10. Phonological awareness instruction should be:
Answer: Explicit and developmentally appropriate.
Rationale: Direct instruction improves literacy outcomes.
Domain 3: Phonics & Word Recognition
11. Phonics instruction teaches students to:
Answer: Connect letters with sounds.
Rationale: Phonics focuses on decoding written language.
12. What is decoding?
Answer: Translating written words into spoken language.
Rationale: Essential for word recognition.
,13. Which strategy supports phonics instruction?
Answer: Systematic and explicit instruction
Rationale: Structured approaches improve mastery.
14. Sight words are:
Answer: High-frequency words recognized automatically.
Rationale: Many cannot be decoded easily using phonics rules.
15. Word families help students:
Answer: Recognize patterns in spelling and sounds.
Rationale: Improves decoding efficiency.
Domain 4: Fluency
16. Reading fluency includes accuracy, rate, and:
Answer: Prosody
Rationale: Expression reflects comprehension.
17. Why is fluency important?
Answer: It allows readers to focus on meaning rather than decoding.
Rationale: Automaticity supports comprehension.
18. Which activity best builds fluency?
Answer: Repeated reading
Rationale: Repetition improves speed and accuracy.
19. Choral reading supports fluency by:
Answer: Reducing anxiety and modeling expression.
Rationale: Group reading builds confidence.
, 20. A fluent reader typically:
Answer: Reads smoothly with appropriate phrasing.
Rationale: Indicates strong decoding skills.
Domain 5: Vocabulary Development
21. Vocabulary instruction should be:
Answer: Intentional and contextualized.
Rationale: Students learn best through meaningful exposure.
22. Tier 2 words are:
Answer: High-utility academic vocabulary words.
Rationale: Common across content areas.
23. Which strategy best supports vocabulary growth?
Answer: Interactive read-alouds
Rationale: Introduces rich language in context.
24. Morphology instruction helps students:
Answer: Understand word meanings through roots and affixes.
Rationale: Supports decoding and comprehension.
25. Repeated exposure to words:
Answer: Strengthens vocabulary retention.
Rationale: Multiple encounters deepen understanding.
Domain 6: Reading Comprehension
26. Reading comprehension is best defined as: