Human Reproduction:
Two separate sexes – male and female.
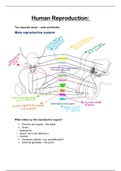
Male reproductive system:
What makes up the reproductive organs?
Primary sex organs – the testis
Ducts:
Epididymis
Sperm duct (vas deferens)
Urethra
Accessory glands - e.g. prostate gland
External genetalia – the penis
,Reproductive Location / definition Function
organ
, Scrotum Contains the testis 1. Regulates temperature,
keeping testis 2 to 3°
lower than body temp.
2. Houses and protect testis
Testis Two oval structures suspended outside of 1. Produce sperm, by the
body in scrotum. germinal layer
Testis consist of many lobules, which 2. Produce testosterone,
contain highly convoluted tubules, the by the interstitial cells.
seminiferous tubules
Germinal epithelium lines the tubules
Between tubules are groups of
endocrine cells, the interstitial cells, or
cells of Leydig.
Ducts Three main ducts:
1. Epididymis Seminiferous tubules join to form the Immature sperm enter
epididymis, a highly convoluted tubule. epididymis where they:
1. mature, to become
motile and fertile
2. are stored for several
months.
2. Sperm Continuation of epididymis. Leaves the 1. Pushes nature sperm
duct scrotum, passes through the prostate gland, forward by strong
and then enters the urethra. peristaltic waves, from
the epididymis into the
urethra – ejaculation.
Peristaltic wave – strong
contraction of smooth muscle
in walls of ducts
3. Urethra Duct at end of the uro-genital system leading Forms common duct for
to the exterior. transportation of semen
and urine, although
these two processes
never occur together.
Prostate gland Plum-sized gland surrounds urethra at base Secretes fluid that aids the
of bladder. transport of the sperm and
contains enzymes that make
sperm more active.
Penis Urethra passes down male external Deposits semen with sperm
organ, penis into female’s vagina during
Consists of special spongy tissue. copulation.
Running the length of penis there are
three sections of erectile tissue.
+ 2 situated on dorsal side
>> corpus cavernosa
+ one on ventral side
>> corpus spongiosum
Erection: dilation of dorsal and central
arteries supplying blood to penis. Allows
for more blood to fill three spongy
erectile tissue chambers. Causing penis
Two separate sexes – male and female.
Male reproductive system:
What makes up the reproductive organs?
Primary sex organs – the testis
Ducts:
Epididymis
Sperm duct (vas deferens)
Urethra
Accessory glands - e.g. prostate gland
External genetalia – the penis
,Reproductive Location / definition Function
organ
, Scrotum Contains the testis 1. Regulates temperature,
keeping testis 2 to 3°
lower than body temp.
2. Houses and protect testis
Testis Two oval structures suspended outside of 1. Produce sperm, by the
body in scrotum. germinal layer
Testis consist of many lobules, which 2. Produce testosterone,
contain highly convoluted tubules, the by the interstitial cells.
seminiferous tubules
Germinal epithelium lines the tubules
Between tubules are groups of
endocrine cells, the interstitial cells, or
cells of Leydig.
Ducts Three main ducts:
1. Epididymis Seminiferous tubules join to form the Immature sperm enter
epididymis, a highly convoluted tubule. epididymis where they:
1. mature, to become
motile and fertile
2. are stored for several
months.
2. Sperm Continuation of epididymis. Leaves the 1. Pushes nature sperm
duct scrotum, passes through the prostate gland, forward by strong
and then enters the urethra. peristaltic waves, from
the epididymis into the
urethra – ejaculation.
Peristaltic wave – strong
contraction of smooth muscle
in walls of ducts
3. Urethra Duct at end of the uro-genital system leading Forms common duct for
to the exterior. transportation of semen
and urine, although
these two processes
never occur together.
Prostate gland Plum-sized gland surrounds urethra at base Secretes fluid that aids the
of bladder. transport of the sperm and
contains enzymes that make
sperm more active.
Penis Urethra passes down male external Deposits semen with sperm
organ, penis into female’s vagina during
Consists of special spongy tissue. copulation.
Running the length of penis there are
three sections of erectile tissue.
+ 2 situated on dorsal side
>> corpus cavernosa
+ one on ventral side
>> corpus spongiosum
Erection: dilation of dorsal and central
arteries supplying blood to penis. Allows
for more blood to fill three spongy
erectile tissue chambers. Causing penis