Simone Zweers
Reference: Brooker, Genetics: Analysis and prinicples, 7th edition
Chapter 5 – Non-Mendelian inheritance
, Genetics summary – VU BMS 2020/2021
Simone Zweers
Reference: Brooker, Genetics: Analysis and prinicples, 7th edition
- Genes that follow a Mendelian inheritance pattern:
o The expression of the genes in the offspring directly influences their traits
o Except in the case of rare mutations, the genes are passed unaltered from
generation to generation
o The genes obey Mendel’s law of segregation
o For crosses involving two or more genes, the genes obey Mendel’s law of
independent assortment
5.1: Maternal effect
The genotype of the mother determines the phenotype of the offspring for maternal effect
genes
- Genes with a maternal effect: the genotype of the mother directly determines the
phenotype of her offspring
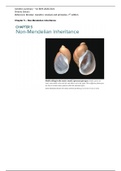
- Shell and internal organs of a water snail can be right- (dextral) or left-handed (sinistral)
o Dextral is more common and dominant
o F1 generation – DD female crossed to dd male, all offspring
were dextral. In the reciprocal cross, dd female and DD
male, all offspring were sinistral no first rule of mendelian
inheritance
o F2 generation – genotype F1 = Dd crossed to each other,
predicted = 1DD:2Dd:1dd 3:1 phenotypic ratio. But the F2
generation were all dextral maternal effect. The
phenotype off the offspring only depends on the genotype of
the mother. D was dominant in the mother so all of the
offspring is dextral
o F3 generation – 3:1 ratio dextral:sinistral dd female
produced a sinistral offspring
Female gametes receive gene products from the mother that affect
early developmental stages of the embryo
- Maternal effect can be explained by the process of oogenesis in female animals
- Oocyte matures surrounding maternal cells (nurse cells) provide the oocyte with
nutrients and other materials
- Heterozygous female meiosis haploid oocyte may receive the D
or d allele, not both
- The surrounding nurse cells produce both
- The gene products of the nurse cells, which reflect the genotype of
the mother, influence the early developmental stages of the embryo
- DD female only transmits D causes the embryo cleavage to occur
in a way that produces a right-handed body plan
- Dd female transmits both D is dominant
- dd female contributes the d left-handed (sperm genotype is
irrelevant; the expression will occur too late
- maternal effect genes often play a role in cell division, cleavage
pattern, and body axis orientation
- defective alleles in maternal genes tend to have dramatic effect on
the phenotype of the offspring, altering major features of morphology,
often with dire consequences
- Drosophila: maternal gene bicoid anterior part embryo