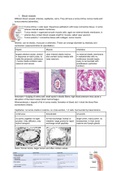
1. Blood vessels
Different blood vessels: Arteries, capillaries, veins. They all have a tunica intima, tunica media and
tunica externa (adventitia).
Tunica intima = outer layer. Squamous epithelium with loose connective tissue. in some
arteries internal elastic membrane
Tunica media = organized smooth muscle cells. again an external elastic membrane, in
arteries they contain blood vessels inself for muscle, called vasa vasorum
Tunica externa = connective tissue with collagen, some muscle.
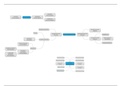
Arteries: can be elastic, muscular or arterioles. These can change diameter by elasticity and
contraction (vasoconstriction & vasodilation).
Elastic Muscle Arterioles
largest arteries (aorta). stretch clear internal elastic lamina. no external elastic membrane.
in response on each pulse, to also contain tunica media with In metarterioles with no
make the pressure continuous vasa vasorum. continuous muscle layers,
> tunica media contains vasa every is surrounded with
vasorum and nerves. endothelium (sphincter
function).
Aneurysm = bulging of artery wall. weak spots in elastic fibers, high blood pressure may cause a
disruption of the blood vessel (brain hemorrhage).
Atherosclerosis = deposit of fat in tunica media, formation of blood clot > block the blood flow
somewhere (infarct).
Capillaries: no tunica media or externa. on cross-section, 1-3 cells. Surrounded by basal lamina.
continuous fenestrated sinusoids
no pores, together via tight for fast exchange, kidney or large lumen, many pores. no
junction. Only diffusion, only intestine. large prores for rapid endosomes. In liver, bone
active transport. exchange small peptides marrow and lymph glands
Veins: thinner tunica, larger lumen and often contain valves.
Different blood vessels: Arteries, capillaries, veins. They all have a tunica intima, tunica media and
tunica externa (adventitia).
Tunica intima = outer layer. Squamous epithelium with loose connective tissue. in some
arteries internal elastic membrane
Tunica media = organized smooth muscle cells. again an external elastic membrane, in
arteries they contain blood vessels inself for muscle, called vasa vasorum
Tunica externa = connective tissue with collagen, some muscle.
Arteries: can be elastic, muscular or arterioles. These can change diameter by elasticity and
contraction (vasoconstriction & vasodilation).
Elastic Muscle Arterioles
largest arteries (aorta). stretch clear internal elastic lamina. no external elastic membrane.
in response on each pulse, to also contain tunica media with In metarterioles with no
make the pressure continuous vasa vasorum. continuous muscle layers,
> tunica media contains vasa every is surrounded with
vasorum and nerves. endothelium (sphincter
function).
Aneurysm = bulging of artery wall. weak spots in elastic fibers, high blood pressure may cause a
disruption of the blood vessel (brain hemorrhage).
Atherosclerosis = deposit of fat in tunica media, formation of blood clot > block the blood flow
somewhere (infarct).
Capillaries: no tunica media or externa. on cross-section, 1-3 cells. Surrounded by basal lamina.
continuous fenestrated sinusoids
no pores, together via tight for fast exchange, kidney or large lumen, many pores. no
junction. Only diffusion, only intestine. large prores for rapid endosomes. In liver, bone
active transport. exchange small peptides marrow and lymph glands
Veins: thinner tunica, larger lumen and often contain valves.