Excretion:
= The removal or elimination of metabolic waste from an organism
= eg. CO2, H2O, bile pigments, urea and mineral salts
Metabolism = chemical reactions that take place within every cell of the body.
Egestion = the removal of undigested food solid waste from the digestive tract
Excretory organs:
Organ Waste product Origin
Lungs Carbon dioxide and water Cellular respiration
vapour
Skin (sweat Mineral salts, traces of urea, Extracted from the blood
glands) water
Liver urea Deamination of excess amino acids
Bile pigments Breakdown of haemoglobin
Colon bile pigments , excess mineral Bile pigments, excess mineral salts from the
salts breakdown of haemoglobin In the liver
Kidney urea Deamination of excess amino acids in the liver
Mineral salts Mineral salts excess taken in with food
Water Excess water consumed and taken in as food
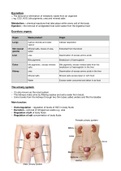
The urinary system:
- it's also known as the renal system.
- The kidneys make urine by ltering wastes and extra water from blood.
- Urine travels from the kidneys through two thin tubes called ureters and lls the bladder.
Main function:
- Osmoregulation – regulation of levels of H2O in body uids
- Excretion – removal of nitrogenous waste e.g. urea
- Regulation of pH of body uids
- Regulation of salt concentration of body uids
Female urinary system
flfi fl fl fi
, The structure of the kidney:
- The kidneys are bean shaped structures
- found half-way down the back just under the ribcage.
- They are protected by adipose (fat) tissue and each kidney is covered by a renal capsule which
protects the kidney and its internal structures from infections.
- Oxygenated Blood with waste products is by the renal artery which branches o the aorta.
- Deoxygenated blood with the waste products removed, leaves the kidney through the renal
vein.
The structure of the kidney:
The structural and functional unit of the kidney:
- The kidneys are highly complex ltration organs.
- Its functional unit is called a nephron
- Nephrons are microscopic coiled structures made up of tubes, arterioles, capillaries and ducts.
- Their main function is to lter the blood, regulate the waste, water and other important
substances the body needs.
- The nephron is divided into two
• the Malpighian body
• the renal tubule.
The nephron:
fi fi ff
= The removal or elimination of metabolic waste from an organism
= eg. CO2, H2O, bile pigments, urea and mineral salts
Metabolism = chemical reactions that take place within every cell of the body.
Egestion = the removal of undigested food solid waste from the digestive tract
Excretory organs:
Organ Waste product Origin
Lungs Carbon dioxide and water Cellular respiration
vapour
Skin (sweat Mineral salts, traces of urea, Extracted from the blood
glands) water
Liver urea Deamination of excess amino acids
Bile pigments Breakdown of haemoglobin
Colon bile pigments , excess mineral Bile pigments, excess mineral salts from the
salts breakdown of haemoglobin In the liver
Kidney urea Deamination of excess amino acids in the liver
Mineral salts Mineral salts excess taken in with food
Water Excess water consumed and taken in as food
The urinary system:
- it's also known as the renal system.
- The kidneys make urine by ltering wastes and extra water from blood.
- Urine travels from the kidneys through two thin tubes called ureters and lls the bladder.
Main function:
- Osmoregulation – regulation of levels of H2O in body uids
- Excretion – removal of nitrogenous waste e.g. urea
- Regulation of pH of body uids
- Regulation of salt concentration of body uids
Female urinary system
flfi fl fl fi
, The structure of the kidney:
- The kidneys are bean shaped structures
- found half-way down the back just under the ribcage.
- They are protected by adipose (fat) tissue and each kidney is covered by a renal capsule which
protects the kidney and its internal structures from infections.
- Oxygenated Blood with waste products is by the renal artery which branches o the aorta.
- Deoxygenated blood with the waste products removed, leaves the kidney through the renal
vein.
The structure of the kidney:
The structural and functional unit of the kidney:
- The kidneys are highly complex ltration organs.
- Its functional unit is called a nephron
- Nephrons are microscopic coiled structures made up of tubes, arterioles, capillaries and ducts.
- Their main function is to lter the blood, regulate the waste, water and other important
substances the body needs.
- The nephron is divided into two
• the Malpighian body
• the renal tubule.
The nephron:
fi fi ff