ila
Sketaltmuscularsystem musdef.br
clavicle cranium
gonist main muscle which contracts during a
movement Sternum
antagonist the opposing muscle to the agonist ribcage
homerous
xator stabolises one part of the body vertebrae
radiog
hip
Phalanges calpais
sotonic during its
contraction
changes length
oncentric shortens while metacarpals
producingtension
femur
centric lengthens while producing tension tibia
sometric muscle contracts but does not fibula talus
change length tarsals
metatarsals
14 t.TW the sequence of events
1 The nerve impulse is initiated in the cell body
2 Nerve impulse is conducted down the axon by the
synaptic cleft
When action potential term
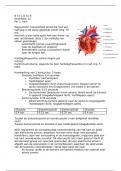
, venous return mechanisms External respiration
pocketvalues gravity exchange of gasses in the lu
restingva.lu smooth muscle respiratory pumps deoxygenatedblood in capillaries a
muscle pumps in thealveoli
HR 725pm
Strokevolume
701 HRregulation
cardiacoutput 521min HRSV Q
coz lacticacid
1 f adrenaline
noradrenaine
internal respiration
diastole Proprio motoractivity exchange ofgasesbetween musclec
relaxation phase
baro stretchvesselwall haemoglobinmoleculesdissociatethe
Systole contraction phase o
t as theypassthemusclecell
p
venousreturn
exercisewhichincreas
breathingfrequency 12 15
a a ton haemoglobin
tiddal volume 5001
de increase in temperature
of minuteventilation 6.7.51min increase productionof CO2
increase lactic carbonicacids lower
ches mechanics of breathing
forkyjefibres
septum
inspiration at rest activeprocess I
ribcage sternum
goes up outbyexternalintercostals
volume in thoracic
scalar shunt cavity pressure withdiaphragm
contracting flattering
gasmoves fromhighto low so ÉÉÉ
rushes in
distribution ofbloodflowfrom one part of thebody
another
onstricts limitingblood flowtothe
alates
capillarybed
inspiration
ribcage
at exercise actin process
sternum
goesup outfromexternalintercostals
j F
maximisingbloodflow tothe capillarybed
Sketaltmuscularsystem musdef.br
clavicle cranium
gonist main muscle which contracts during a
movement Sternum
antagonist the opposing muscle to the agonist ribcage
homerous
xator stabolises one part of the body vertebrae
radiog
hip
Phalanges calpais
sotonic during its
contraction
changes length
oncentric shortens while metacarpals
producingtension
femur
centric lengthens while producing tension tibia
sometric muscle contracts but does not fibula talus
change length tarsals
metatarsals
14 t.TW the sequence of events
1 The nerve impulse is initiated in the cell body
2 Nerve impulse is conducted down the axon by the
synaptic cleft
When action potential term
, venous return mechanisms External respiration
pocketvalues gravity exchange of gasses in the lu
restingva.lu smooth muscle respiratory pumps deoxygenatedblood in capillaries a
muscle pumps in thealveoli
HR 725pm
Strokevolume
701 HRregulation
cardiacoutput 521min HRSV Q
coz lacticacid
1 f adrenaline
noradrenaine
internal respiration
diastole Proprio motoractivity exchange ofgasesbetween musclec
relaxation phase
baro stretchvesselwall haemoglobinmoleculesdissociatethe
Systole contraction phase o
t as theypassthemusclecell
p
venousreturn
exercisewhichincreas
breathingfrequency 12 15
a a ton haemoglobin
tiddal volume 5001
de increase in temperature
of minuteventilation 6.7.51min increase productionof CO2
increase lactic carbonicacids lower
ches mechanics of breathing
forkyjefibres
septum
inspiration at rest activeprocess I
ribcage sternum
goes up outbyexternalintercostals
volume in thoracic
scalar shunt cavity pressure withdiaphragm
contracting flattering
gasmoves fromhighto low so ÉÉÉ
rushes in
distribution ofbloodflowfrom one part of thebody
another
onstricts limitingblood flowtothe
alates
capillarybed
inspiration
ribcage
at exercise actin process
sternum
goesup outfromexternalintercostals
j F
maximisingbloodflow tothe capillarybed