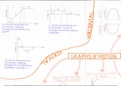
Collision Theory
Bella 14/10/2022
● For chemical reactions to appen, the reactants need to collide with energy greater or
equal to the activation energy and the correct orientation.
● For a successful collision, the collision geometry must be right. The reactant
molecules have to be facing the right way.
● Activation energy: The minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur
● Reactant molecules have enough kinetic energy to collide successfully and
overcome the repulsion caused by outer electrons
● If the activation energy is high for a reaction, only a few particles will have enough
energy to collide so the reaction will be slow
● If a reaction has a low activation energy ten the reaction will be fats as lots of
particles will have the necessary energy
Alternating factors of a reaction:
● Temperature- If the temperature increases the particles have more energy so move
more frequently.
● Concentration- If the concentration is increased there are more reactant particles
colliding. So the reaction rate is increased. The higher the concentration the faster
the rate of reaction.
● Pressure- If the pressure of gas reactants is increased, there are more reactant
particles for a given volume. The higher the pressure the faster reaction rate.
● Particle size- By decreasing the particle size you are increasing the surface area. A
smaller particle size provides greater surface area that collisions can take place on.
● Catalysts- A catalyst can provide a surface for the reaction, the reactants molecules
are held at favourable angles for collisions increasing successful collisions
likelyhood.
Only some of the collisions that take place cause a chemical reaction to happen. These are
successful collisions. The greater the number of collisions, the faster the reaction.
A catalyst alters reaction rates, it allows the reaction to occur at lower temperatures.
Therefore, catalysts are used in the chemical industry to make manufacturing more
economical. Nickel – to make margarine by hardening vegetable oil. This process is called
hydrogenation, it increases the melting point of fats and oils improving its oxidation
resistance and flavour deterioration. Other examples include:Iron- making ammonia by the
haber process and platinum to manufacture nitric acid.
Bella 14/10/2022
● For chemical reactions to appen, the reactants need to collide with energy greater or
equal to the activation energy and the correct orientation.
● For a successful collision, the collision geometry must be right. The reactant
molecules have to be facing the right way.
● Activation energy: The minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur
● Reactant molecules have enough kinetic energy to collide successfully and
overcome the repulsion caused by outer electrons
● If the activation energy is high for a reaction, only a few particles will have enough
energy to collide so the reaction will be slow
● If a reaction has a low activation energy ten the reaction will be fats as lots of
particles will have the necessary energy
Alternating factors of a reaction:
● Temperature- If the temperature increases the particles have more energy so move
more frequently.
● Concentration- If the concentration is increased there are more reactant particles
colliding. So the reaction rate is increased. The higher the concentration the faster
the rate of reaction.
● Pressure- If the pressure of gas reactants is increased, there are more reactant
particles for a given volume. The higher the pressure the faster reaction rate.
● Particle size- By decreasing the particle size you are increasing the surface area. A
smaller particle size provides greater surface area that collisions can take place on.
● Catalysts- A catalyst can provide a surface for the reaction, the reactants molecules
are held at favourable angles for collisions increasing successful collisions
likelyhood.
Only some of the collisions that take place cause a chemical reaction to happen. These are
successful collisions. The greater the number of collisions, the faster the reaction.
A catalyst alters reaction rates, it allows the reaction to occur at lower temperatures.
Therefore, catalysts are used in the chemical industry to make manufacturing more
economical. Nickel – to make margarine by hardening vegetable oil. This process is called
hydrogenation, it increases the melting point of fats and oils improving its oxidation
resistance and flavour deterioration. Other examples include:Iron- making ammonia by the
haber process and platinum to manufacture nitric acid.