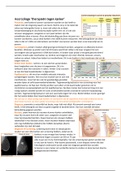
CASE STUDY: NILE DELTA, EGYPT – ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
• 39 million people Why was Aswan dam built and what are consequences on
• Pop density: 1000 ppl/km2 water and sediment supply to delta?
• Alexandria has 4.5 mn • Aswan Dam - large prestige infrastructure project for
people, largest city on Delta Egypt . Create employment opps in farming, tourism
• Delta = area of intense and secondary industry , provide irrigation and water
farming supply for country mostly desert.
• Aswan Dam constructed on • Lake Nassar created behind dam to kick start economy
Nile river 1 100km away by creating cheap HEP and encourage FDI
from mouth of river • Took 10 years to build and opened in 1970.
Changes to the Nile Delta sediment budget (due to construction of Aswan Dam):
• Reduction in amount of sediment accreted , from 120 mn tonnes/year to only trace amounts
today.
• Caused sig changes along shoreline of NW Nile Delta - accelerated erosion and rates of coastal
retreat as high as 148 m/year.
What economic developments have taken place on delta in past 25 yrs. and why?
Fish Farm Expansion:
• 1990: 81km of delta used as fish farms..2014 - 937 km2.
• Spatial distribution and pattern of fish breeding farms are mostly conc. around Lake Burullus
(31%).
• People benefit from being close to sea - pump sea water into artificial ponds - used to breed fish.
• Fish farming = crucial economic activity for Egypt, initially expanded due to population growth in
70’s but expanded further as a commercial enterprise and one of Egypt’s main food exports.
Urban Growth:
• One of the major problems in Egypt and Nile Delta.
• Coastal zone has shown major urban growths that extensively expanded to cover about
1686 km2 in 2014. In 1990 urbanized area ltd to about 250 km2.
• Road construction along coastal zone in 2014 was about 2900 km - increased by about 35% in last
25 years. Such infrastructure development was another accelerating factor for changing land use
in study area particularly for urban and fish farming due to easy accessibility.
Agriculture:
• Nile Delta characterized by agricultural land - accommodates +55% of total pop in Egypt. In 1990
about 50% of coastal zone occupied by agriculture lands (3233 km2) – 2014: 2268 km2
• Mainly due to extensive transformation of land uses into other usage activities
• Practices not been sustainable. Intensification e.g. overgrazing activities of date palm farms at
Damietta, Rosetta and wood storage areas (near Damietta Harbour) = degradation of land.
• Intensification was result of ↑agricultural productivity = national food security.
Shoreline changes:
Rosetta promontory:
• Coastal shoreline retreat at mouth of Rosetta: 820 m - av. annual rate of recession now
25 m/year.
• Despite construction of groynes to E of Rosetta, erosion detected - area now experiences
controversial phases of accretion and erosion - shoreline advancement of +40 m/yr and a retreat
of −8.5 m/yr. Groynes constructed too close to each other - small interval distances b/n.
Damietta promontory:
• Shoreline retreat at mouth of Damietta is 1330 m – av. annual rate of recession is 36 m/year.
• Sediment eroded from Damietta carried by current (W-E) and deposited in spit system.
• Downdrift of Damietta promontory, ↑rates of deposition and advancement of spit system
reaching a maximum of 1002 m length with an average yearly growth rate of 28 m/year.
Rising Sea Levels in the Med of 1.2 mm/year have contributed to ↑erosion rates as deeper water = larger
waves with ↑amounts of energy and these reach further inland.
• 39 million people Why was Aswan dam built and what are consequences on
• Pop density: 1000 ppl/km2 water and sediment supply to delta?
• Alexandria has 4.5 mn • Aswan Dam - large prestige infrastructure project for
people, largest city on Delta Egypt . Create employment opps in farming, tourism
• Delta = area of intense and secondary industry , provide irrigation and water
farming supply for country mostly desert.
• Aswan Dam constructed on • Lake Nassar created behind dam to kick start economy
Nile river 1 100km away by creating cheap HEP and encourage FDI
from mouth of river • Took 10 years to build and opened in 1970.
Changes to the Nile Delta sediment budget (due to construction of Aswan Dam):
• Reduction in amount of sediment accreted , from 120 mn tonnes/year to only trace amounts
today.
• Caused sig changes along shoreline of NW Nile Delta - accelerated erosion and rates of coastal
retreat as high as 148 m/year.
What economic developments have taken place on delta in past 25 yrs. and why?
Fish Farm Expansion:
• 1990: 81km of delta used as fish farms..2014 - 937 km2.
• Spatial distribution and pattern of fish breeding farms are mostly conc. around Lake Burullus
(31%).
• People benefit from being close to sea - pump sea water into artificial ponds - used to breed fish.
• Fish farming = crucial economic activity for Egypt, initially expanded due to population growth in
70’s but expanded further as a commercial enterprise and one of Egypt’s main food exports.
Urban Growth:
• One of the major problems in Egypt and Nile Delta.
• Coastal zone has shown major urban growths that extensively expanded to cover about
1686 km2 in 2014. In 1990 urbanized area ltd to about 250 km2.
• Road construction along coastal zone in 2014 was about 2900 km - increased by about 35% in last
25 years. Such infrastructure development was another accelerating factor for changing land use
in study area particularly for urban and fish farming due to easy accessibility.
Agriculture:
• Nile Delta characterized by agricultural land - accommodates +55% of total pop in Egypt. In 1990
about 50% of coastal zone occupied by agriculture lands (3233 km2) – 2014: 2268 km2
• Mainly due to extensive transformation of land uses into other usage activities
• Practices not been sustainable. Intensification e.g. overgrazing activities of date palm farms at
Damietta, Rosetta and wood storage areas (near Damietta Harbour) = degradation of land.
• Intensification was result of ↑agricultural productivity = national food security.
Shoreline changes:
Rosetta promontory:
• Coastal shoreline retreat at mouth of Rosetta: 820 m - av. annual rate of recession now
25 m/year.
• Despite construction of groynes to E of Rosetta, erosion detected - area now experiences
controversial phases of accretion and erosion - shoreline advancement of +40 m/yr and a retreat
of −8.5 m/yr. Groynes constructed too close to each other - small interval distances b/n.
Damietta promontory:
• Shoreline retreat at mouth of Damietta is 1330 m – av. annual rate of recession is 36 m/year.
• Sediment eroded from Damietta carried by current (W-E) and deposited in spit system.
• Downdrift of Damietta promontory, ↑rates of deposition and advancement of spit system
reaching a maximum of 1002 m length with an average yearly growth rate of 28 m/year.
Rising Sea Levels in the Med of 1.2 mm/year have contributed to ↑erosion rates as deeper water = larger
waves with ↑amounts of energy and these reach further inland.