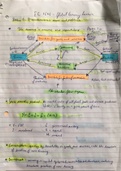
● The first stage of anaerobic + aerobic respiration
● Occurs in cytoplasm + is an anaerobic process
2.describe the process of glycolysis
● Glucose (6C) is phosphorylated to glucose phosphate (6C), using ATP
● Glucose phosphate splits into 2 triose phosphate (3C)
● TP (3C) is oxidised to form pyruvate (3C) + NAD is reduced to NADH + there is a net
gain of 2 ATP
3. What are the products of glycolysis?
● 2x pyruvate
● Net gain of 2 ATP- we made 4, however 2 ATP had to be used initially at stage 1
● 2x NADH
4.Describe the process of the link reaction:
● Pyruvate (3C) is oxidised to acetate (2C)
● NAD is reduced to NADH + CO2 is released
● Acetate combines with coenzyme A to produce acetyl coenzyme A
5. In the link reaction, what are the products for every glucose molecule?
● 2x acetyl CoA
● 2 CO2 released
● 2 reduced NAD
6. What happens in the Krebs cycle?
● acetyl coenzyme A (2C) reacts with a 4C molecule, releasing coA + producing a 6C
molecule that enters the Krebs cycle
● In a series of oxidation- reduction reactions, the Krebs cycle generates reduced
coenzymes + ATP by substrate- level phosphorylation + CO2 is lost —> FAD reduced to
FADH, NAD reduced to NADH
● Produces energy in the form of ATP + produces coenzymes
7. What are the products per cycle of the Krebs cycle
● 3x reduced NAD
● 1x reduced FAD
● 1x ATP
● 2x CO2
, 8. What are the products of the Krebs cycle per glucose molecule
● 6x reduced NAD
● 2x reduced FAD
● 2x ATP
● 4x CO2
9.where does link reaction take place?
● Mitochondria
10.where does krebs cycle take place?
● Mitochondrial matrix
11.how can proteins be used in aerobic resp?
● Forms pyruvate + acetyl coA in aerobic resp to produce ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosimotic theory)
● Reduced FAD and reduced NAD transfer electrons to ETC
● Electrons are passed along the ETC
● Energy is lost
● Energy lost is used to actively transport H+ from mitochondrial matrix into the inter
membrane space
● This creates electrochemical gradient in the inter membrane space
● H+ diffuse through ATP synthase, producing ATP as ADP + Pi is combined
● H+ combine with O2 forming water (reverse photolysis)
● O2 is the final e- acceptor
where does oxidative phosphorylation take place?
● Intermembrane space
Why is oxidative phosphorylation important?
● O2 is the final electron acceptor
● Important for ATP production, which is needed for metabolism in cells
Anaerobic respiration
1.where does anaerobic respiration occur?
● Cytoplasm of cell only
2.what is the fermentation equation for bacteria + yeast?
● Pyruvate —--> ethanol + CO2