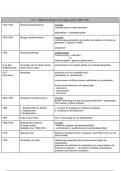
Occupiers’ Liability
An occupier of premises may be liable in tort to a claimant who suffers personal injury or
property damage whilst on those premises.
Occupiers’ liability is governed by two Acts:
- The Occupiers’ Liability Act (1957) (OLA 1957) which is concerned with the duty of
care owed to all lawful visitors.
- The Occupiers’ Liability Act (1984) (OLA 1984) which is concerned with the duty owed
to people other than lawful visitors. Usually these others will be trespassers.
This tort developed from negligence; similar.
S1 (1) – Occupier’s liability arises from loss or injury caused by the state of the premises or
things done to them, not by activities carried out on premises.
Fairchild v Glenhaven Funeral Services [2002] – the Court of Appeal held that the claimant’s
contact with asbestos dust at work was a result of an activity carried out on the premises rather
than their static state.
Tomlinson v Congleton BC [2003] – the danger was not due to the ’state of the premises, or
things done or omitted to be done on them’
Therefore, it appears to be that the OLA 1957 and OLA 1984 only cover loss arising from the
state of the premises and not from the activities carried out on the premises. Loss or damage
arising from such activities or other causes than the state of the premises should be claimed
under negligence (Siddorn v Patel [2007]); Poppleton v Trustees of Portsmouth Youth Activities
Committee [2008]
Definition of Occupier:
No definition is given in either Act. However, the test for determining who an occupier is can be
found in common law.
Wheat v E Lacon & Co Ltd [1966] – the courts appear to have taken a broad approach, holding
that a person will be an occupier if he has a sufficient degree of control over the state of the
premises.
Lord Denning identified 4 categories of occupier:
1) A landlord who lets premises; he has parted with control of the premises so the tenant
will be the occupier
An occupier of premises may be liable in tort to a claimant who suffers personal injury or
property damage whilst on those premises.
Occupiers’ liability is governed by two Acts:
- The Occupiers’ Liability Act (1957) (OLA 1957) which is concerned with the duty of
care owed to all lawful visitors.
- The Occupiers’ Liability Act (1984) (OLA 1984) which is concerned with the duty owed
to people other than lawful visitors. Usually these others will be trespassers.
This tort developed from negligence; similar.
S1 (1) – Occupier’s liability arises from loss or injury caused by the state of the premises or
things done to them, not by activities carried out on premises.
Fairchild v Glenhaven Funeral Services [2002] – the Court of Appeal held that the claimant’s
contact with asbestos dust at work was a result of an activity carried out on the premises rather
than their static state.
Tomlinson v Congleton BC [2003] – the danger was not due to the ’state of the premises, or
things done or omitted to be done on them’
Therefore, it appears to be that the OLA 1957 and OLA 1984 only cover loss arising from the
state of the premises and not from the activities carried out on the premises. Loss or damage
arising from such activities or other causes than the state of the premises should be claimed
under negligence (Siddorn v Patel [2007]); Poppleton v Trustees of Portsmouth Youth Activities
Committee [2008]
Definition of Occupier:
No definition is given in either Act. However, the test for determining who an occupier is can be
found in common law.
Wheat v E Lacon & Co Ltd [1966] – the courts appear to have taken a broad approach, holding
that a person will be an occupier if he has a sufficient degree of control over the state of the
premises.
Lord Denning identified 4 categories of occupier:
1) A landlord who lets premises; he has parted with control of the premises so the tenant
will be the occupier