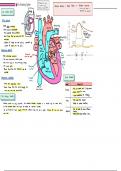
The Circulatory System
Stretch iness of aor ta
crucial to
Heart Rate Stroke Volume
is
slowly Cardiac Output = ✗
flatten out blood pressure ( How
.
much blood is
The Cardiac Cycle % ejected per beat)
/ ←✗ ← , - --
%
Superior
I - - ,
" """ "
" "
"
• Both
a_a contract .
Pulmonary
-
Atria volume decreases . \
→ pressure in
.
This increases atria pressure .
aor taexceeds
ventricles ( valves
-
Blood flows from the atria into the close to prevent
backflow
)
ventricles .
← Vein
-
Backflow of blood into the veins is prevented by
closure of valves into the veins .
Ventricular systole
sinoatrial
Mitral
Both ventricles contract ]
'
node CSA node
Valve
-
The atrio -
ventricular values close
Left Aortic
Semi lunar valves in the
pulmonary artery
•
valve
and aorta open Pulmonary
.
-
Blood flows from the ventricles into the Valve
arteries .
Ventricular Diastole Tricuspid
Valve
Blood
xx -
Vessels
- - - -
%
Atria and ventricles relax
'
vessel characteristics
Blood flows from the reins the Inferior
through
-
Vena cava
• Thick and muscular wall high pressure)
atria and into the ventricles Arteries
.
tissue for recoil
• Elastic
for
The cardiac Muscle %
•
Folded endothelium stretching
1=-31--1 , - , -
% veins
•
Wider lumen than arteries
-
Cardiac muscle not
only contracts ,
but conducts electrical impulses in a similar
way
to nerve cells .
'
Valves to prevent backflow
•
It has branched fibres which assist the spread of electrical impulses .
-
It can function at lower
oxygen
levels than skeletal mivscle and has a higher tolerance for CO2 and lactic
.
One cell thick for short diffusion
capillaries pathway
levels
acid .
.
Capillary beds increase surface area
?⃝
Stretch iness of aor ta
crucial to
Heart Rate Stroke Volume
is
slowly Cardiac Output = ✗
flatten out blood pressure ( How
.
much blood is
The Cardiac Cycle % ejected per beat)
/ ←✗ ← , - --
%
Superior
I - - ,
" """ "
" "
"
• Both
a_a contract .
Pulmonary
-
Atria volume decreases . \
→ pressure in
.
This increases atria pressure .
aor taexceeds
ventricles ( valves
-
Blood flows from the atria into the close to prevent
backflow
)
ventricles .
← Vein
-
Backflow of blood into the veins is prevented by
closure of valves into the veins .
Ventricular systole
sinoatrial
Mitral
Both ventricles contract ]
'
node CSA node
Valve
-
The atrio -
ventricular values close
Left Aortic
Semi lunar valves in the
pulmonary artery
•
valve
and aorta open Pulmonary
.
-
Blood flows from the ventricles into the Valve
arteries .
Ventricular Diastole Tricuspid
Valve
Blood
xx -
Vessels
- - - -
%
Atria and ventricles relax
'
vessel characteristics
Blood flows from the reins the Inferior
through
-
Vena cava
• Thick and muscular wall high pressure)
atria and into the ventricles Arteries
.
tissue for recoil
• Elastic
for
The cardiac Muscle %
•
Folded endothelium stretching
1=-31--1 , - , -
% veins
•
Wider lumen than arteries
-
Cardiac muscle not
only contracts ,
but conducts electrical impulses in a similar
way
to nerve cells .
'
Valves to prevent backflow
•
It has branched fibres which assist the spread of electrical impulses .
-
It can function at lower
oxygen
levels than skeletal mivscle and has a higher tolerance for CO2 and lactic
.
One cell thick for short diffusion
capillaries pathway
levels
acid .
.
Capillary beds increase surface area
?⃝