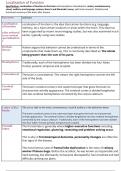
autonomic)
The nervous system
The divisions of the nervous system: central and peripheral (somatic & autonomic)
Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous Systems
Consists of the Brain & Spinal cord (PNS)
- cerebral cortex in higher mental functions / conscious awareness (I Comprises of two sub-systems,
realised that...) somatic and autonomic
- decision making (...I decided to run.)
- auditory cortex / temporal lobe in processing auditory information (...
I heard footsteps behind me…)
- visual cortex / occipital lobe in processing visual information
(I saw a bus...)
PNS
(Somatic + Autonomic)
Somatic Autonomic
● Part of PNS ● Part of PNS
● SNS has sensory and motor pathways ● ANS is purely motor pathways
● Connects motor impulses from the CNS to ● Connects motor impulses from the CNS to the
the skeletal muscles and the senses cardiac muscle, smooth muscle in gut & glands
● Controls voluntary (conscious) responses & internal organs
● Eg. walking, picking something up, playing ● Controls involuntary (unconscious) responses
the guitar ● Eg. heart rate, breathing rate, hormone
production, digestion, pupil size
ANS
(Sympathetic & Parasympathetic)
Sympathetic Parasympathetic
● Hypothalamus prepares the body for action/emergency response AKA ● parasympathetic NS will
fight or flight response start to restore the
● Involves the release of adrenaline (from the adrenal gland/medulla). body’s response
● Triggers/activates/switches from parasympathetic to sympathetic ● Slows heart and relaxes
activity and back again. muscles
● Aim to calm the body
Role of adrenaline: down activates ‘rest &
• Adrenaline is released from the adrenal medulla in response to activation digest’
of the sympathomedullary pathway.
• Adrenaline has a range of effects on the body
• Direct effects of adrenaline
– increase heart rate
– constricts blood vessels, increasing rate of blood flow and raising blood
pressure
– diverts blood away from the skin, kidneys and digestive system
– increases blood to brain and skeletal muscle
– increases respiration and sweating
• The general effects of adrenaline
– prepare the body for action, fight or flight,
– increase blood supply/oxygen, to skeletal muscle for physical action
– increase oxygen to brain for rapid response planning