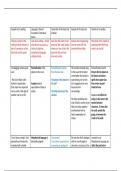
Learning approaches - Behaviourism
The main assumption of behaviourism is that (+)Behaviourism was the first truly scientific way of studying
psychology with reliable, objective methods --> we can prove
behaviour in humans and animals is a result of
cause and effect relationships between stimulus and response.
learning, or conditioning. Classical conditioning
(Pavlov) is learning through association. (+)The focus on nurture implies that people can change -->
positive as behavioural shaping can be used as a force for good.
- A neutral stimulus, something that provokes no
(+)Real world applications of behaviourist theory -->
response eg bell
understanding gambling and other addictive behaviours --> two
- Becomes a conditioned stimulus
process model is a successful explanation for simple phobias
- When it is paired with an unconditioned stimulus
eg food
(-)The approach is environmentally deterministic --> implies that
- Which is something that already produces an
people have no choice in how they behave --> behaviourism
unconditioned response eg salivation
provides limited explanations which cannot take into account
- The response becomes a conditioned response.
subjective mental states such as thoughts and emotions.
Research Methods
(-)It attempts to apply scientific reductionism to human behaviour,
Behaviourists use laboratory experiments with
breaking down complex responses to simple laws of conditioning.
animals such as dogs, rats and pigeons, to strictly
This neglects many levels of explanation of human psychology
control the conditions of learning and scientifically
that are thought to be very important by other researchers, such as
demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships.
cognitions, emotions and relationships.
The main assumption of behaviourism is that (+)Behaviourism was the first truly scientific way of studying
psychology with reliable, objective methods --> we can prove
behaviour in humans and animals is a result of
cause and effect relationships between stimulus and response.
learning, or conditioning. Classical conditioning
(Pavlov) is learning through association. (+)The focus on nurture implies that people can change -->
positive as behavioural shaping can be used as a force for good.
- A neutral stimulus, something that provokes no
(+)Real world applications of behaviourist theory -->
response eg bell
understanding gambling and other addictive behaviours --> two
- Becomes a conditioned stimulus
process model is a successful explanation for simple phobias
- When it is paired with an unconditioned stimulus
eg food
(-)The approach is environmentally deterministic --> implies that
- Which is something that already produces an
people have no choice in how they behave --> behaviourism
unconditioned response eg salivation
provides limited explanations which cannot take into account
- The response becomes a conditioned response.
subjective mental states such as thoughts and emotions.
Research Methods
(-)It attempts to apply scientific reductionism to human behaviour,
Behaviourists use laboratory experiments with
breaking down complex responses to simple laws of conditioning.
animals such as dogs, rats and pigeons, to strictly
This neglects many levels of explanation of human psychology
control the conditions of learning and scientifically
that are thought to be very important by other researchers, such as
demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships.
cognitions, emotions and relationships.