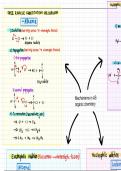
Evaluation of Genetic Explanation of Criminal Behaviour
Reductionist Explanation
The genetic explanation is better at explaining violent or aggressive crimes because candidate genes, such as
the MAOA gene co for this behaviour. But not all crimes are violent. For example, theft and drug us don’t
have to be violent.
This means that the genetic explanation alone is an incomplete explanation of criminal behaviour.
Crime is a Social Construction
People have created a category of behaviour deemed criminal and this includes many different types of
crime. This means that what is considered criminal can (&has) changed over time. For example,
homosexuality at one point was considered illegal but now it is not. It also means that what is classed as
criminal can differ around the world, as different social groups may have different ideas about the types of
behaviour they consider unacceptable and ought to be illegal. For example, marijuana use is illegal in the
UK but legal in Amsterdam.
It is difficult to argue that crime has a genetic cause when genetics are believed to cause a range of
behaviours; society’s ideas about what behaviour constitutes clinal behaviour changes more quickly than
genetics do; and different cultural groups are likely to have similar genetics.
Problems with deterministic explanations
Genetic explanations are presented as if the genes a person is born with with determine their later behaviour.
But criminality cannot be entirely explained in terms of genetics, otherwise concordance rates for MZ twins
in twin studies (such as Raine, 1993) would be 100%, not 53%.
Tiihonen et al (2015) found that people with the MAOA and CDH13 genes were 13x more likely to commit
crime. This doesn’t guarantee that all people with these genes commit crime; just that the probability that
they will is high.
Practical Applications
If it is known that some people have MAOA and/or CDH13 genes and/or who have criminal biological
parents, criminal adoptive parents or are brought up in a dysfunctional family; interventions could be put in
place to try to prevent criminal behaviour from occurring.
This means that knowledge of the genetic explanation of criminal behaviour can help direct limited
services/resources, to where they will have the greatest impact. This will have positive economic
implications and benefit society (if less crime were committed as a result).
Problems with twin studies
Problems with twin studies such as Christianson (1977) who found a 35% concordance rate of criminal
behaviour for MZ twins and 13% concordance rate for criminal behaviour for DZ twins amongst 3586 twin
pairs.
Both MZ & DZ twins are normally raised in the same environment. This means that it is difficult to establish
if the higher concordance rate for MZ twins is due to their shared genetics (nature) or their shared
environment (nurture).
In addition, concordance rates are not 100%, which indicates that there must be something else other than
biology (I.e. environmental) contributing to this behaviour.
Problems with adoption studies
Problems with adoption studies such as Mednick et al (1987) who found that 15% of sons adopted by a
criminal family went on to commit crime in comparison to 20% of sons who had a biological parent who
committed crime.
Many children experience late donation and still maintain contact with their biological parents. This means
that many children may still have learnt their criminal behaviour from their biological parents rather than it
being attributable to their genetics. This means that the role of nurture cannot be ruled out from adoption
studies.
Reductionist Explanation
The genetic explanation is better at explaining violent or aggressive crimes because candidate genes, such as
the MAOA gene co for this behaviour. But not all crimes are violent. For example, theft and drug us don’t
have to be violent.
This means that the genetic explanation alone is an incomplete explanation of criminal behaviour.
Crime is a Social Construction
People have created a category of behaviour deemed criminal and this includes many different types of
crime. This means that what is considered criminal can (&has) changed over time. For example,
homosexuality at one point was considered illegal but now it is not. It also means that what is classed as
criminal can differ around the world, as different social groups may have different ideas about the types of
behaviour they consider unacceptable and ought to be illegal. For example, marijuana use is illegal in the
UK but legal in Amsterdam.
It is difficult to argue that crime has a genetic cause when genetics are believed to cause a range of
behaviours; society’s ideas about what behaviour constitutes clinal behaviour changes more quickly than
genetics do; and different cultural groups are likely to have similar genetics.
Problems with deterministic explanations
Genetic explanations are presented as if the genes a person is born with with determine their later behaviour.
But criminality cannot be entirely explained in terms of genetics, otherwise concordance rates for MZ twins
in twin studies (such as Raine, 1993) would be 100%, not 53%.
Tiihonen et al (2015) found that people with the MAOA and CDH13 genes were 13x more likely to commit
crime. This doesn’t guarantee that all people with these genes commit crime; just that the probability that
they will is high.
Practical Applications
If it is known that some people have MAOA and/or CDH13 genes and/or who have criminal biological
parents, criminal adoptive parents or are brought up in a dysfunctional family; interventions could be put in
place to try to prevent criminal behaviour from occurring.
This means that knowledge of the genetic explanation of criminal behaviour can help direct limited
services/resources, to where they will have the greatest impact. This will have positive economic
implications and benefit society (if less crime were committed as a result).
Problems with twin studies
Problems with twin studies such as Christianson (1977) who found a 35% concordance rate of criminal
behaviour for MZ twins and 13% concordance rate for criminal behaviour for DZ twins amongst 3586 twin
pairs.
Both MZ & DZ twins are normally raised in the same environment. This means that it is difficult to establish
if the higher concordance rate for MZ twins is due to their shared genetics (nature) or their shared
environment (nurture).
In addition, concordance rates are not 100%, which indicates that there must be something else other than
biology (I.e. environmental) contributing to this behaviour.
Problems with adoption studies
Problems with adoption studies such as Mednick et al (1987) who found that 15% of sons adopted by a
criminal family went on to commit crime in comparison to 20% of sons who had a biological parent who
committed crime.
Many children experience late donation and still maintain contact with their biological parents. This means
that many children may still have learnt their criminal behaviour from their biological parents rather than it
being attributable to their genetics. This means that the role of nurture cannot be ruled out from adoption
studies.