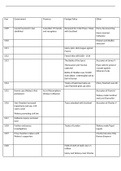
Titration steps
1. All apparatus rinsed with distilled water and then with relevant solution
2. Using a pipette and pipette filler, pipette 25cm3 of NaOH into a conical flask and
touch surface of solution with tip to ensure correct quantity is transferred
3. Using a funnel, fill burette with acid and then remove funnel
4. Otherwise, some drops may fall through titration so a lower volume will be recorded
than used
5. Allow a small quantity of acid to flow through the burette to ensure jet space is filled.
Note initial reading on burette
6. If jet space not filled titre volume will be higher than volume actually added
7. Add 2-3 drops of PP no place white tile so you can see colour change better
8. Add acid from burette into conical flask swirling mixture during addition until
indicator changes colour
9. During titration rinse sides of conical flask with water to ensure all acid is in solution
10. Note reading and repeat but add acid dropwise
11. Continue repeating until at least two concordant results are obtained
Miscellaneous facts
Optical isomer = non-superimposable mirror images
Stereoisomerism = two or more compounds have the same structural formula but they differ
in the arrangement of bonds in space
H2SO4 + HNO3 to NO2+ H2SO4 + H2O
Sodium Oxide + water = Sodium hydroxide with a pH of 12-14.
Phosphorous Oxide in water gives a pH of 1-2
Molecules are a group of atoms bonded to covalent bonds
Alkaline hydrolysis is a nucleophilic addition elimination reaction
AGI contains covalent character and forces holding lattice together are actually stronger
Silicon, phosphorus, sulphur, and chlorine oxides are acidic
m/z = 31 is due to CH2OH+ ion
Standard concentration is a solution of known concentration
1. All apparatus rinsed with distilled water and then with relevant solution
2. Using a pipette and pipette filler, pipette 25cm3 of NaOH into a conical flask and
touch surface of solution with tip to ensure correct quantity is transferred
3. Using a funnel, fill burette with acid and then remove funnel
4. Otherwise, some drops may fall through titration so a lower volume will be recorded
than used
5. Allow a small quantity of acid to flow through the burette to ensure jet space is filled.
Note initial reading on burette
6. If jet space not filled titre volume will be higher than volume actually added
7. Add 2-3 drops of PP no place white tile so you can see colour change better
8. Add acid from burette into conical flask swirling mixture during addition until
indicator changes colour
9. During titration rinse sides of conical flask with water to ensure all acid is in solution
10. Note reading and repeat but add acid dropwise
11. Continue repeating until at least two concordant results are obtained
Miscellaneous facts
Optical isomer = non-superimposable mirror images
Stereoisomerism = two or more compounds have the same structural formula but they differ
in the arrangement of bonds in space
H2SO4 + HNO3 to NO2+ H2SO4 + H2O
Sodium Oxide + water = Sodium hydroxide with a pH of 12-14.
Phosphorous Oxide in water gives a pH of 1-2
Molecules are a group of atoms bonded to covalent bonds
Alkaline hydrolysis is a nucleophilic addition elimination reaction
AGI contains covalent character and forces holding lattice together are actually stronger
Silicon, phosphorus, sulphur, and chlorine oxides are acidic
m/z = 31 is due to CH2OH+ ion
Standard concentration is a solution of known concentration