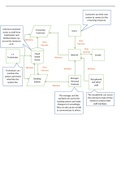
IMMUNITY ÷÷Y¥÷÷÷÷:÷
$
Monocytes
antibodies
. sauna..
Innate -
@ non -
specific defencewithin hours
play immediately or
mech come into
.
of Innate
§! *
u
monocytes → macrophages
antigen 's appearance ( phagocytosis)
.
@ composed of specialised
cues +
Adaptive eliminate pathogens -1
-
processes that
¥29
+ is
highly
creates immunological memory
to particular pathogen
.
specific
antibody mediated
→
② Cell mediated
specific Immunity * unmediated T lymphocytes -
-0A bone marrow Cmature
in thymus gland)
① Antibody mediated in cells
( lymph ) mature in nodes * targets antigens already
B- Lymphocytes ⑤
-
bone marrow
> infected cells
cells)
antibodies on it 's (turnout cancer
each unique B cell done carries
specific
antibodies combine with specific antigen IB
surface -
> abnormal self antigens
transplanted foreign tissue antigens
cell
surface
-
when these >
is ACTIVATED ISENSITISED
Hdd stimulus weak ( no memory cells)
÷ into
secretes protein perforin . causes sores
to form
g¥ge{ima }
mitosis
÷ rapidly by ST Killer •
-
.
better if it combines with a macrophage in target cell membrane
Jama
aatnsion
mceeqygty e
G,
8
that has phagocytesed the antigen
1- is an APC
to
> + helper
@ stimulate B an -
immflamation
-
+
differentiation ,
phagocytosis by producing
T-cell :-,
do Hodak 4 cytokines
Eg
antibodies
)
circulate for antigen presenting au
-
. >
T -
suppressor cells
-
o stop BTT responses after infection
garobuindetifahl'id response detects antigen it's
upon re
-
exposure If T -
lymphocyte stmemoryceees
B r T -
helper cells are produced
↳ Thayer cells interact with macrophage APC
* antibodies target free # r release which stimulate
CYTOKINES
antigens B cells to differentiate
-
←
how antibodies work
menu
-
he Immune System has Memory a
to immune response B cell ( takes time)
antigen o must contact
specific
- -
Ab
specific comrdlimeutaey pathogen forming Ag complex
-
bind to ,
20 immune response -0 Starts as soon as
memory " cells encounter
antigen
① Agglutination → 2nd
↳ 1st exposure
Abaood . more rapid Gnc
'
have 2 binding sites
cross link . antigens forming clumps exposure
> easier to ahagocytose
TYPES of Immunity
> d spread
hero auction otaathogens (pcaantaycoeostral )
transfer
>
nfbnutratirseaaitniosieson antigen
virus binds to host
•
-
makes it
ineffective caaigiciaeexaosureaniliwa.LI#pqnatural
antigen e'9-
Passive
vaccine ?
Active
e. g. site where # antibodies given ( short term)
1.
# ↳
Hotifinal
¥
⑤
( Oppsonisation
make the natural
easier
Abs attach to antigen phagocytes
can
identify them antibodies ( )
,
infection themselves
Blood Groups types g- vaccine
.
plasma
cserumerans )
-
k
clotting factors
.
first 6 months Abd
§§.tl?e!aYed-oweakened'
te" antis' "
"" " ""
"
fqqr-n.fi A " b Already infected
Femininity -
.
¥gYug7yMuimggg÷.us
eyed
cells Ab levels
booster vaccines keep
high
'
memory tetanus
* donors antigen
e -
g. ,
ebdajabs > natwauy denature
Grotius)
recipients
antibody # overtime
B
a - can test
for many conditions
fffgffeeninrema
B pa
Belman amal )
-
antibodies
f•i•
atone .
lmmunosorbant
,
is
a
assay
① mouse infected with particular antigen
plate wells absorbed onto matrix ② B- cells removed
surface of
in each well
g. specific Abs
.
cells (promote rapid :-O
③ hybridise d with cancer
AB Sample
of
added
of body fluid Ags
A as source
-
f universal
IBBY Bi long life)
.
recipient Abr
Ag reactor
triggers enzyme
to cause colour
change identifying Ag
: .
k B
'
as Agon plate ,
vigaatient has Abs these win bind ④ cultured in
made
,
Extracted
fermentedas ramified -
detect pathogens
detect
uses : >
cancer cell markers ⑤ termed monsoonal they're aurel 't tyre
>
markers than trad Frans
⑦ purer
serum
o b a
universal > detect cardiac disease
Houff J donor
pregnancy
tests
be @ rod in large quantities
£
>
④ can
.
2nd
Cytokinefor Detection
specific enzyme
a
Ab with
→
b b
e e e
attaagengaenwymenanagaysesareaaion immflammation
biomarker
→ Ag areseat in serum or urine used to detect Rheumatoid Arthritis
hormone in blood lurine HCG Abs on ELISA
HCG .
colour
I Btk Atha
Ag binding olinked enzyme change
o
Ab
- - .
plate Monoclonal Abs
-
→
.
$
Monocytes
antibodies
. sauna..
Innate -
@ non -
specific defencewithin hours
play immediately or
mech come into
.
of Innate
§! *
u
monocytes → macrophages
antigen 's appearance ( phagocytosis)
.
@ composed of specialised
cues +
Adaptive eliminate pathogens -1
-
processes that
¥29
+ is
highly
creates immunological memory
to particular pathogen
.
specific
antibody mediated
→
② Cell mediated
specific Immunity * unmediated T lymphocytes -
-0A bone marrow Cmature
in thymus gland)
① Antibody mediated in cells
( lymph ) mature in nodes * targets antigens already
B- Lymphocytes ⑤
-
bone marrow
> infected cells
cells)
antibodies on it 's (turnout cancer
each unique B cell done carries
specific
antibodies combine with specific antigen IB
surface -
> abnormal self antigens
transplanted foreign tissue antigens
cell
surface
-
when these >
is ACTIVATED ISENSITISED
Hdd stimulus weak ( no memory cells)
÷ into
secretes protein perforin . causes sores
to form
g¥ge{ima }
mitosis
÷ rapidly by ST Killer •
-
.
better if it combines with a macrophage in target cell membrane
Jama
aatnsion
mceeqygty e
G,
8
that has phagocytesed the antigen
1- is an APC
to
> + helper
@ stimulate B an -
immflamation
-
+
differentiation ,
phagocytosis by producing
T-cell :-,
do Hodak 4 cytokines
Eg
antibodies
)
circulate for antigen presenting au
-
. >
T -
suppressor cells
-
o stop BTT responses after infection
garobuindetifahl'id response detects antigen it's
upon re
-
exposure If T -
lymphocyte stmemoryceees
B r T -
helper cells are produced
↳ Thayer cells interact with macrophage APC
* antibodies target free # r release which stimulate
CYTOKINES
antigens B cells to differentiate
-
←
how antibodies work
menu
-
he Immune System has Memory a
to immune response B cell ( takes time)
antigen o must contact
specific
- -
Ab
specific comrdlimeutaey pathogen forming Ag complex
-
bind to ,
20 immune response -0 Starts as soon as
memory " cells encounter
antigen
① Agglutination → 2nd
↳ 1st exposure
Abaood . more rapid Gnc
'
have 2 binding sites
cross link . antigens forming clumps exposure
> easier to ahagocytose
TYPES of Immunity
> d spread
hero auction otaathogens (pcaantaycoeostral )
transfer
>
nfbnutratirseaaitniosieson antigen
virus binds to host
•
-
makes it
ineffective caaigiciaeexaosureaniliwa.LI#pqnatural
antigen e'9-
Passive
vaccine ?
Active
e. g. site where # antibodies given ( short term)
1.
# ↳
Hotifinal
¥
⑤
( Oppsonisation
make the natural
easier
Abs attach to antigen phagocytes
can
identify them antibodies ( )
,
infection themselves
Blood Groups types g- vaccine
.
plasma
cserumerans )
-
k
clotting factors
.
first 6 months Abd
§§.tl?e!aYed-oweakened'
te" antis' "
"" " ""
"
fqqr-n.fi A " b Already infected
Femininity -
.
¥gYug7yMuimggg÷.us
eyed
cells Ab levels
booster vaccines keep
high
'
memory tetanus
* donors antigen
e -
g. ,
ebdajabs > natwauy denature
Grotius)
recipients
antibody # overtime
B
a - can test
for many conditions
fffgffeeninrema
B pa
Belman amal )
-
antibodies
f•i•
atone .
lmmunosorbant
,
is
a
assay
① mouse infected with particular antigen
plate wells absorbed onto matrix ② B- cells removed
surface of
in each well
g. specific Abs
.
cells (promote rapid :-O
③ hybridise d with cancer
AB Sample
of
added
of body fluid Ags
A as source
-
f universal
IBBY Bi long life)
.
recipient Abr
Ag reactor
triggers enzyme
to cause colour
change identifying Ag
: .
k B
'
as Agon plate ,
vigaatient has Abs these win bind ④ cultured in
made
,
Extracted
fermentedas ramified -
detect pathogens
detect
uses : >
cancer cell markers ⑤ termed monsoonal they're aurel 't tyre
>
markers than trad Frans
⑦ purer
serum
o b a
universal > detect cardiac disease
Houff J donor
pregnancy
tests
be @ rod in large quantities
£
>
④ can
.
2nd
Cytokinefor Detection
specific enzyme
a
Ab with
→
b b
e e e
attaagengaenwymenanagaysesareaaion immflammation
biomarker
→ Ag areseat in serum or urine used to detect Rheumatoid Arthritis
hormone in blood lurine HCG Abs on ELISA
HCG .
colour
I Btk Atha
Ag binding olinked enzyme change
o
Ab
- - .
plate Monoclonal Abs
-
→
.