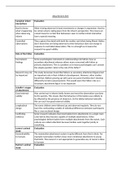
Attachment A03
Caregiver infant Evaluation
interactions
Hard to know What is being observed is hand movements or changes in expression. Hard to
what’s happening be certain what is taking place from the infant’s perspective. This means we
when observing cannot know for certain that behaviours seen in mother-infant interaction
infants have a special meaning.
Controlled They capture fine detail with both the mother and infant being filmed. Babies
observations don’t know they are being observed so their behaviour does not change in
response to controlled observation. This is a strength as it means the
research has good validity
Role of the father Evaluation
Inconsistent Some psychologists interested in understanding role fathers have as
findings secondary attachment whereas others more concerned with father as
primary attachment. This is a problem as it means psychologists can’t answer
the simple question ‘what is the role of the father?’
Research may not The study Grossman found that fathers as secondary attachment figures had
be important an important role in their children’s development. However, other studies
found that children growing up with same-sex parent families don’t develop
differently to hetro-sexual parents. This would seem the fathers role as a
secondary attachment figure is not important.
Schaffer’s stages Evaluation
of attachment
Good external Was carried out in infants family homes and most the observation was done
validity by the parents. This means that the behaviour of the babies was unlikely to
be affected by the presence of observers. So the babies behaved naturally.
We can say it has good external validity
Longitudinal The same children were followed up and observed regularly. They do not
design have the confounding variable of individual differences between participants
like a cross-sectional design.
Conflicting Some research indicates that most babies form attachments to a single main
evidence carer before they become capable of multiple attachments. Other
psychologists believe babies form multiple attachments from the outset. Such
cultures are called collectivist because families work together jointly in
everything.
Lorenz’s animal Evaluation
study
Generalisability The mammalian attachment system is quite different from that in birds. For
to humans example mammalian mothers show more emotional attachment to young
that birds. This means it is not appropriate to generalise any of Lorenz’s ideas
to humans
Harlow’s animal Evaluation
study
Caregiver infant Evaluation
interactions
Hard to know What is being observed is hand movements or changes in expression. Hard to
what’s happening be certain what is taking place from the infant’s perspective. This means we
when observing cannot know for certain that behaviours seen in mother-infant interaction
infants have a special meaning.
Controlled They capture fine detail with both the mother and infant being filmed. Babies
observations don’t know they are being observed so their behaviour does not change in
response to controlled observation. This is a strength as it means the
research has good validity
Role of the father Evaluation
Inconsistent Some psychologists interested in understanding role fathers have as
findings secondary attachment whereas others more concerned with father as
primary attachment. This is a problem as it means psychologists can’t answer
the simple question ‘what is the role of the father?’
Research may not The study Grossman found that fathers as secondary attachment figures had
be important an important role in their children’s development. However, other studies
found that children growing up with same-sex parent families don’t develop
differently to hetro-sexual parents. This would seem the fathers role as a
secondary attachment figure is not important.
Schaffer’s stages Evaluation
of attachment
Good external Was carried out in infants family homes and most the observation was done
validity by the parents. This means that the behaviour of the babies was unlikely to
be affected by the presence of observers. So the babies behaved naturally.
We can say it has good external validity
Longitudinal The same children were followed up and observed regularly. They do not
design have the confounding variable of individual differences between participants
like a cross-sectional design.
Conflicting Some research indicates that most babies form attachments to a single main
evidence carer before they become capable of multiple attachments. Other
psychologists believe babies form multiple attachments from the outset. Such
cultures are called collectivist because families work together jointly in
everything.
Lorenz’s animal Evaluation
study
Generalisability The mammalian attachment system is quite different from that in birds. For
to humans example mammalian mothers show more emotional attachment to young
that birds. This means it is not appropriate to generalise any of Lorenz’s ideas
to humans
Harlow’s animal Evaluation
study