https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cK-OGB1_ELE
Gene silencing happens during translation (mRNA).
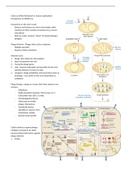
Control of Gene Expression (changes):
1. Transcription - DNA transcription to RNA, RNA polymerase
a. Promoters
b. Regulatory regions e.g.: enhancer sequences
c. Transcription factors
d. Chromatin –histone modifications
e. DNA methylation
2. Translation - mRNA (nucleotide) translation to protein (peptides,
amino acids)
a. Gene silencing
b. Ribosome
c. Protein synthesis
d. Initiation factors
3. Post translational - Protein function and turnover
a. Post translational modifications – sticking things to peptides
i. Ubiquitination targets protein for degradation
ii. Phosphorylation regulates protein function
miRNA: single stranded and involved in gene silencing
LncRNA: long non-coding RNA
RNAi: interferes RNA during translation and it’s a naturally occurring
process - use reverse transcription and qPCR for an assay of RNAi
You think gene C is important in process Y?
- How could you investigate this?
- What are you really asking?
- Is gene X functionally relevant?
Clinical applications:
Patisiran/ ONPATTRO is approved for a rare peripheral nerve disease:
, - Hereditary transthyretin (hATTR) amyloidosis
- Inherited mutations in the transthyretin (TTR) gene.
- The liver produces abnormal TTR protein
- Mutant TTR protein accumulates as deposits in body tissues (amyloidosis).
- These deposits disrupt the structure and damage the function of affected tissues.
Mechanism of action:
- Patisiran Is a double-stranded small interfering RNA
- Targets a sequence within the transthyretin (TTR) mRNA that is conserved across wild-type and all TTR variants
- Patisiran reduces production of mutant and wild-type TTR by the liver.
siRNA therapies are in development:
The discovery of RNA interference:
- 1984– Izant, J. & Weintraub, H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene
expression by antisense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic
analysis.Cell36, 1007–1015
- This was a useful experimental tool, but how did it work?
- 1998– Fire et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Nature 391,
806–811
- “Anti-sensing” or RNAi of a target gene is more efficient with
dsRNA
How does RNA interference work?
Gene silencing happens during translation (mRNA).
Control of Gene Expression (changes):
1. Transcription - DNA transcription to RNA, RNA polymerase
a. Promoters
b. Regulatory regions e.g.: enhancer sequences
c. Transcription factors
d. Chromatin –histone modifications
e. DNA methylation
2. Translation - mRNA (nucleotide) translation to protein (peptides,
amino acids)
a. Gene silencing
b. Ribosome
c. Protein synthesis
d. Initiation factors
3. Post translational - Protein function and turnover
a. Post translational modifications – sticking things to peptides
i. Ubiquitination targets protein for degradation
ii. Phosphorylation regulates protein function
miRNA: single stranded and involved in gene silencing
LncRNA: long non-coding RNA
RNAi: interferes RNA during translation and it’s a naturally occurring
process - use reverse transcription and qPCR for an assay of RNAi
You think gene C is important in process Y?
- How could you investigate this?
- What are you really asking?
- Is gene X functionally relevant?
Clinical applications:
Patisiran/ ONPATTRO is approved for a rare peripheral nerve disease:
, - Hereditary transthyretin (hATTR) amyloidosis
- Inherited mutations in the transthyretin (TTR) gene.
- The liver produces abnormal TTR protein
- Mutant TTR protein accumulates as deposits in body tissues (amyloidosis).
- These deposits disrupt the structure and damage the function of affected tissues.
Mechanism of action:
- Patisiran Is a double-stranded small interfering RNA
- Targets a sequence within the transthyretin (TTR) mRNA that is conserved across wild-type and all TTR variants
- Patisiran reduces production of mutant and wild-type TTR by the liver.
siRNA therapies are in development:
The discovery of RNA interference:
- 1984– Izant, J. & Weintraub, H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene
expression by antisense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic
analysis.Cell36, 1007–1015
- This was a useful experimental tool, but how did it work?
- 1998– Fire et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Nature 391,
806–811
- “Anti-sensing” or RNAi of a target gene is more efficient with
dsRNA
How does RNA interference work?