,Keywords
• GENEOTYPE – the genetic makeup of an organism
• PHENOTYPE – the characteristics of an organism determined by genes and
influenced by the environment
• GENE – sequence of DNA that codes for a single protein
• ALLELIC FREQUENCY – the number of times that an allele occurs within the
gene pool
• GENE POOL – total number of alleles of genes in a population
• DOMINANT ALLELE – expressed in phenotype regardless of allele on other
chromosome
• RECESSIVE ALLELE – expressed in phenotype if alleles on both chromosom
are the same (homozygous)
,Monohybrid inheritance
• MONOHYBRID INHERITANCE = the inheritance of a single gene
,Inheritance of pod colour in peas
• EXAMPLE - Mendel studied the colour of the pods of pea plants – t
come in 2 colours (green and yellow)
• If pea plants with green pods breed together = they are pure –
breeding for the character of green pods (homozygous)
• If the pure- breeding green pod and pure- breeding yellow pod bre
together, the offspring (F1 generation) will have green pods.
• This means the allele for green pods is dominant and the allele for
yellow pods is recessive
,
,
,What is the expected ratio for a
monohybrid cross?
• 3:1
,Dihybrid inheritance
• DIHYBRID INHERITANCE = inheritance of two genes located on
different chromosomes
,
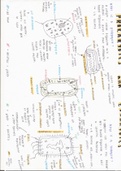
, Dihybrid inheritance
• RG and rg are linked
• RrGg individuals produce RG and rg gametes
• As the chromosomes arrange themselves at random on the equato
during meiosis, any one of the two alleles of the gene for seed colo
(G and g) can combine with any one of the alleles for seed shape (R
and r)
• Crossing over occurs which produces a small amount of Rg and rG
gametes
• Fewer individuals with Rrgg and rrGg