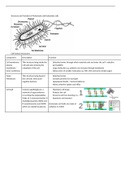
Structure and Function of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
Cell-Surface Structures:
Component Description Function
Cell membrane / Thin structure lying inside the - Selective barrier through which materials exit and enter the cell = selective
plasma cell wall and enclosing the permeability
membrane / cytoplasm of the cell. - Large molecules e.g. proteins can not pass through membrane
inner membrane - Allows entry of smaller molecules e.g. H20, CO2 and some simple sugars
Outer Thin structure lying beyond - Selective barrier
Membrane the cell wall. Only Gram- - Contains proteins for transport
negative bacteria - Lipopolysaccharide – bacterial defence
- Allows selective uptake and efflux
Cell wall Contains peptidoglycan, a - Maintains cell shape
network of sugar polymers - Protects the cell
cross linked by polypeptides. - Prevents cell from bursting in a
Made of 2 monosaccharides N hypotonic environment
Acetylglucosamine (NAG) and
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) (Eukaryote cell walls are made of
which are related to glucose. cellulose or chitin)
, (Archaea contain polysaccharides and proteins but lack
peptidoglycan). Gram stain used to classify bacteria by cell
wall composition:
- Gram-positive bacteria have simpler walls with a large
amount of peptidoglycan
- Gram-negative bacteria have less peptidoglycan and
an outer membrane that contains lipopolysaccharides
Cell-Surface Structures:
Component Description Function
Cell membrane / Thin structure lying inside the - Selective barrier through which materials exit and enter the cell = selective
plasma cell wall and enclosing the permeability
membrane / cytoplasm of the cell. - Large molecules e.g. proteins can not pass through membrane
inner membrane - Allows entry of smaller molecules e.g. H20, CO2 and some simple sugars
Outer Thin structure lying beyond - Selective barrier
Membrane the cell wall. Only Gram- - Contains proteins for transport
negative bacteria - Lipopolysaccharide – bacterial defence
- Allows selective uptake and efflux
Cell wall Contains peptidoglycan, a - Maintains cell shape
network of sugar polymers - Protects the cell
cross linked by polypeptides. - Prevents cell from bursting in a
Made of 2 monosaccharides N hypotonic environment
Acetylglucosamine (NAG) and
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) (Eukaryote cell walls are made of
which are related to glucose. cellulose or chitin)
, (Archaea contain polysaccharides and proteins but lack
peptidoglycan). Gram stain used to classify bacteria by cell
wall composition:
- Gram-positive bacteria have simpler walls with a large
amount of peptidoglycan
- Gram-negative bacteria have less peptidoglycan and
an outer membrane that contains lipopolysaccharides