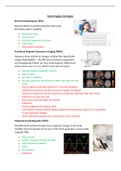
Brain Imaging Techniques
Electroencephalogram (EEG):
Records electrical activity along the scalp using
electrodes and an amplifier.
Relatively cheap
Non-invasive
Excellent temporal resolution
Easy to use
Poor spatial resolution
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI):
Measures brain activity by changes in blood flow (specifically
oxygen/haemoglobin – the differences between oxygenated
and deoxygenated blood has very small magnetic differences),
when a brain area is in use, blood in that area increases.
Detailed spatial resolution (1-6mm)
Non-invasive
No risks of radiation
Has the capacity to demonstrate entire networks of brain
areas
Poor temporal resolution (delay of 2-5 seconds between
activation of neurons and the increase in oxygen rich blood)
Some tiny clusters of neurons may be too small to be detected (less than 3mm)
Patient has to stay very still
Very noisy (uncomfortable for patient)
Expensive
Need a magnetically isolated room
Is an indirect measure (BOLD (blood oxygen level dependent) signal) so is susceptible
to non-neuronal changes
Some individuals may get very stressed out in the machine
Magnetoencephalography (MEG):
Identifies brain activity through micro magnetic changes in the brain,
multiple neurons together in one area of the brain generates a measurable
magnetic field.
Non-invasive
A direct measure of brain function
High temporal resolution
Silent
No radiation
Expensive
Electroencephalogram (EEG):
Records electrical activity along the scalp using
electrodes and an amplifier.
Relatively cheap
Non-invasive
Excellent temporal resolution
Easy to use
Poor spatial resolution
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI):
Measures brain activity by changes in blood flow (specifically
oxygen/haemoglobin – the differences between oxygenated
and deoxygenated blood has very small magnetic differences),
when a brain area is in use, blood in that area increases.
Detailed spatial resolution (1-6mm)
Non-invasive
No risks of radiation
Has the capacity to demonstrate entire networks of brain
areas
Poor temporal resolution (delay of 2-5 seconds between
activation of neurons and the increase in oxygen rich blood)
Some tiny clusters of neurons may be too small to be detected (less than 3mm)
Patient has to stay very still
Very noisy (uncomfortable for patient)
Expensive
Need a magnetically isolated room
Is an indirect measure (BOLD (blood oxygen level dependent) signal) so is susceptible
to non-neuronal changes
Some individuals may get very stressed out in the machine
Magnetoencephalography (MEG):
Identifies brain activity through micro magnetic changes in the brain,
multiple neurons together in one area of the brain generates a measurable
magnetic field.
Non-invasive
A direct measure of brain function
High temporal resolution
Silent
No radiation
Expensive