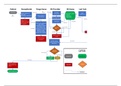
Growth and Development in Plants
Responding to the Environment – Plants
Growth and development in plants are controlled by Hormones. There are three main groups
of plant hormones: Namely: - Auxins, Gibberellins, Abscisic acid.
Auxins:
Auxins bring about a bending reaction in plants known as tropism.
Functions:
Stimulate cell elongation.
Stimulate cell division (But only in the presence of other plant hormones)
Stimulate the development of adventitious roots.
Causes Tropism
Gibberellins:
Functions:
Stimulates stem elongation.
Stimulate root growth.
Promote flowering.
Promote the growth of lateral buds.
Stimulate the germination of seeds.
Abscisic Acid:
Abscisic acid is a growth inhibitor that counteracts the functioning of auxins. It plays a role in
helping the plant to cope under stressful conditions. It is produced in leaves, stems, and
unripe fruit.
Function of Abscisic acid:
Causes dormancy of terminal buds and lateral buds in winter.
Contributes to the dormancy of seeds by inhibiting germination.
Promotes the abscission (detachment) of leaves and fruit.
Causes the closing of stoma when the plant wilts (drying out)
Tropism
Responding to the Environment – Plants
Growth and development in plants are controlled by Hormones. There are three main groups
of plant hormones: Namely: - Auxins, Gibberellins, Abscisic acid.
Auxins:
Auxins bring about a bending reaction in plants known as tropism.
Functions:
Stimulate cell elongation.
Stimulate cell division (But only in the presence of other plant hormones)
Stimulate the development of adventitious roots.
Causes Tropism
Gibberellins:
Functions:
Stimulates stem elongation.
Stimulate root growth.
Promote flowering.
Promote the growth of lateral buds.
Stimulate the germination of seeds.
Abscisic Acid:
Abscisic acid is a growth inhibitor that counteracts the functioning of auxins. It plays a role in
helping the plant to cope under stressful conditions. It is produced in leaves, stems, and
unripe fruit.
Function of Abscisic acid:
Causes dormancy of terminal buds and lateral buds in winter.
Contributes to the dormancy of seeds by inhibiting germination.
Promotes the abscission (detachment) of leaves and fruit.
Causes the closing of stoma when the plant wilts (drying out)
Tropism