Properties of tests and items
psychological tests :
systematic procedure comparing behavior a c r o s s individuals
maximum performance tests :
m e s s u re skills
typical performancet e s ts :
m e ss u re traits
power t e s t s : without time
pressure
speed lests :
time pressure
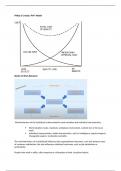
va r i a n c e in test s c o re s enhances test's ability to differentiate between individuals
p-value :
proportion correct
3-value :
proportion incorrect specific a n swe r
>
-
ideal item performance p
=
q
= 0 . 5
9-value : total proportion incorrect
Transformed s c o re s and norms
criterion - referenced transformation :
compare to fixed standards
norm-referenced transformation :
c o m p a re to population norms
linear transformations : maintain shape of s c o re distributions and correlation ,
z- s c o re s
n on -lin e ar transformations : Issume normal distribution ,
aller s c o re shopes ,
normalized z- s c o re s
Objectivity
objectivity e n s u re s consistency
s c ro ss restors
inter-rater reliability : messured by Cohen's Kapps , adjusts for agreement expected by chance .
>
-
k closer 1
to signifies higher reliability ,
crucial for high-stakeslests.
, Reliability
Reliability :
degree to which test s c o re s
very when he test is administered at least twice under equal conditions
to the some
person .
G:
rxx =
>
- SF not directly observable
Classical test theory :
separating the systematic part from the random port
true s c o re
:
lest a c ro ss
larges m o u n t of replications
average s c o re
single individual - Ei = o
,
SE : = SXi
population >
- Sx" =
St + Se ,
o = Rxx11
Se equal for !
everyone
Methods to estimate reliability :
test-retest reliability test twice Correlation between two sets of s c o re s the
gives
:
measuring some .
reliability estimate
>
- Rxx =
Rx exz
parallel forms reliability : two different ve r s i o n s of > test thatass u me d to m e s s u re the some construct .
the correlation
between s c o re s from these ve r s i o n s estimates reliability
>
-
Rxx =
Rxexz ,
if not pomolle R(x + x2) <
Rxx
·
i n te r n a l
consistency methods :
split-hell method for half test with parallel forms method without knowing whole
Reliability reliability
:
, .
(row) Cronbach's alpha :
average split-half reliability for all possible ways of splitting
standardized Cronbach's alphs : Row alphs for standardized items
KR-20 :
reliability coefficient for dichotomous items , always equal to
Row Cronbach's alphs
- IC methods decent indication of reliability for unidimensional lests but underestimates reliability
gives ,
for multidimensional lests .
if confidence intervals do not overlap ,
he s c o re s differ significantly .
if overlap ,
not sufficient to differentiate between s c o re s .
Factors influencing reliability
1 .
quality of items (internal consistency
2 .
dimensionality
psychological tests :
systematic procedure comparing behavior a c r o s s individuals
maximum performance tests :
m e s s u re skills
typical performancet e s ts :
m e ss u re traits
power t e s t s : without time
pressure
speed lests :
time pressure
va r i a n c e in test s c o re s enhances test's ability to differentiate between individuals
p-value :
proportion correct
3-value :
proportion incorrect specific a n swe r
>
-
ideal item performance p
=
q
= 0 . 5
9-value : total proportion incorrect
Transformed s c o re s and norms
criterion - referenced transformation :
compare to fixed standards
norm-referenced transformation :
c o m p a re to population norms
linear transformations : maintain shape of s c o re distributions and correlation ,
z- s c o re s
n on -lin e ar transformations : Issume normal distribution ,
aller s c o re shopes ,
normalized z- s c o re s
Objectivity
objectivity e n s u re s consistency
s c ro ss restors
inter-rater reliability : messured by Cohen's Kapps , adjusts for agreement expected by chance .
>
-
k closer 1
to signifies higher reliability ,
crucial for high-stakeslests.
, Reliability
Reliability :
degree to which test s c o re s
very when he test is administered at least twice under equal conditions
to the some
person .
G:
rxx =
>
- SF not directly observable
Classical test theory :
separating the systematic part from the random port
true s c o re
:
lest a c ro ss
larges m o u n t of replications
average s c o re
single individual - Ei = o
,
SE : = SXi
population >
- Sx" =
St + Se ,
o = Rxx11
Se equal for !
everyone
Methods to estimate reliability :
test-retest reliability test twice Correlation between two sets of s c o re s the
gives
:
measuring some .
reliability estimate
>
- Rxx =
Rx exz
parallel forms reliability : two different ve r s i o n s of > test thatass u me d to m e s s u re the some construct .
the correlation
between s c o re s from these ve r s i o n s estimates reliability
>
-
Rxx =
Rxexz ,
if not pomolle R(x + x2) <
Rxx
·
i n te r n a l
consistency methods :
split-hell method for half test with parallel forms method without knowing whole
Reliability reliability
:
, .
(row) Cronbach's alpha :
average split-half reliability for all possible ways of splitting
standardized Cronbach's alphs : Row alphs for standardized items
KR-20 :
reliability coefficient for dichotomous items , always equal to
Row Cronbach's alphs
- IC methods decent indication of reliability for unidimensional lests but underestimates reliability
gives ,
for multidimensional lests .
if confidence intervals do not overlap ,
he s c o re s differ significantly .
if overlap ,
not sufficient to differentiate between s c o re s .
Factors influencing reliability
1 .
quality of items (internal consistency
2 .
dimensionality