Communication within a neuron
The message spread within a neuron is an electrical event action potential
The membrane of a neuron is generally – 70 mV
compared to the outside, changes in this voltage
lead to an electrical message.
The charge of the membrane = membrane potential
Resting potential = ± -70 mV
This resting potential is maintained by the
sodium-potassium pump. (active, ATP)
3 Na+ out & 2 K+ in
Inside less
positive,
relatively
negative
When the resting
potential is in place the
following
concentrations are
present in and out of
the cell
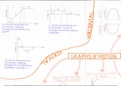
When resting potential is raised up to ± -55 mV threshold is met.
Due to previous action potentials/stimuli
A strong depolarization (process of getting more a more positive in the intracellular
environment compared to the outside) takes place.
(voltage dependent) Na+ channels open, positive ions (cations) flow in. Membrane
gets more positive compared to the outside external environment.
Flow of Na+ into the cell due to electrostatic pressure. (positive Na+ into negative
intracellular environment)
and concentration gradient. (location with a high concentration Na+, moves Na+ to a
location with a lower concentration)
Repolarization comes into play when
K+ channels open. These transfer K+ out of the cell.
Concentration gradient causes this K+ to move out because there are very little K+
ions in the extracellular area and very many inside the membrane.
the both electrostatic pressure & concentration gradient influence Na+ outflow, whereas
only the concentration gradient affect K+. Na+ channels work stronger
Na+ channels become refractory no more movement of Na+
, Hyperpolarization
K+ channels remain open for quite long, much K+ flows
out
Inside becomes even more negative than -70 mV
Refractory period
Absolute refractory period = impossible to elicit a second
action potential
Relative refractory period = it is possible to fire a neuron
again but only when stimulation is extremely high (since
it’s still hyperpolarized)
This refractory period allows a message to move in 1
way only
Refractory period is basis of the rate law (strong stimulus higher rate of action
potentials)
Reparation of the resting potential
Sodium potassium pump actively restores membrane potential
Laws
- All-or-none law
= an action potential either occurs or not. When it does occur it always has the same
size (within one axon). Action potential sizes may vary per axon.
- Rate law
= a strong stimulus high rate of action potentials (not a big/high action potential.
Axonal conduction
Conduction of action potentials are non-decremental (do not grow weaker)
Conduction starts @ axon hillock (exit axon from soma) propagation of action potential
In myelinated axons, ions can only pass the membrane at the nodes of ranvier. the signal
gets somewhat weaker while traveling the myelinated areas, but still strong enough to open
voltage dependent channels.
In essence the elicited action potentials will still be occurring in the same strength, but
merely at the nodes of ranvier.
The action potential ‘hops’ from node to node Saltatory conduction
Myelination
High speed due to saltatory conduction
Economic benefit (less energy is consumed by sodium potassium transporters <ions
cannot move there>)