DCL Task 4. Word learning
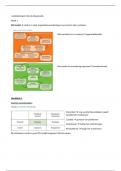
Learning goals
1. Influence of perceptual system on word learning
2. Two different mechanisms before and after word spurt
3. ERP study of Torkildson
4. Individual differences in word learning
5. N400-priming effect and relation to word learning
Werker
Word learning requires a complex mapping among a concept and the word’s corresponding
acoustic signal. Bootstrapping: using existing knowledge to facilitate acquisition of novel
abilities. The perceptual biases infants have at birth serve as the ‘primitives’ from which word
forms are constructed. General perceptual learning enables infants to extract these early word
forms, using increasingly precise knowledge of the acoustic and phonetic properties of the
native language. These word forms become more stable once they are linked with concepts.
Initial perceptual bias
Initial biases (preferring mothers voice and native langage) and capabilities (to discriminate
languages with different rhythmical properties and early-appearing categorical-like
discrimination of phonetic contrasts) prepare the perceptual system for later speech input from
the environment.
Initial neural organization in neonates has some specificity for speech signals, but requires
further experience to establish adult-like organization. By 10-12m, infants show adult-like left
hemisphere dominance for speech. However, limited plasticity is also seen. Damage to the left
hemisphere in infancy can lead to similar areas in the right hemisphere taking over the
phonetic tasks. Neural and perceptual systems are initially organized to treat speech sounds
differently from non-speech, but are also dependent on experience.
Native language reorganizes perceptual sensitivity, selectively maximizing attention to
phonetic features that distinguish native language categories. Newborns can discriminate both
native and non-native phonetic contrasts, but by 6–12 months of age show a decline in
discrimination of many non-native distinctions and an enhancement of sensitivity to native
ones. Changes in perceptual sensitivity during the first year are called ‘functional
reorganization; developing patterns of discrimination in accordance with functional categories
in the native language. One mechanism that underlies functional reorganization might be
statistical; specific properties of input (frequency, distribution) may shape the perceptual
system. When phonetic contrasts are high in frequency, children categorize these quicker.
Infants must learn to recognize and represent contrasting acoustic forms of words.
Word segmentation. Infants begin to segment words by 7–8 months of age. At 7 months,
English-learning infants pull out words that conform to the common English strong-weak
stress pattern, like ‘DOCtor’, but do not segment weakstrong words like ‘guiTAR’, this
happens by 10 months. Once learned, frequent word forms, facilitate segmentation of new
words. Another statistical regularity that infants are sensitive to is ‘transitional probability’,
learning that syllables from within one word are more likely to co-occur than syllables from
separate words.
Learning goals
1. Influence of perceptual system on word learning
2. Two different mechanisms before and after word spurt
3. ERP study of Torkildson
4. Individual differences in word learning
5. N400-priming effect and relation to word learning
Werker
Word learning requires a complex mapping among a concept and the word’s corresponding
acoustic signal. Bootstrapping: using existing knowledge to facilitate acquisition of novel
abilities. The perceptual biases infants have at birth serve as the ‘primitives’ from which word
forms are constructed. General perceptual learning enables infants to extract these early word
forms, using increasingly precise knowledge of the acoustic and phonetic properties of the
native language. These word forms become more stable once they are linked with concepts.
Initial perceptual bias
Initial biases (preferring mothers voice and native langage) and capabilities (to discriminate
languages with different rhythmical properties and early-appearing categorical-like
discrimination of phonetic contrasts) prepare the perceptual system for later speech input from
the environment.
Initial neural organization in neonates has some specificity for speech signals, but requires
further experience to establish adult-like organization. By 10-12m, infants show adult-like left
hemisphere dominance for speech. However, limited plasticity is also seen. Damage to the left
hemisphere in infancy can lead to similar areas in the right hemisphere taking over the
phonetic tasks. Neural and perceptual systems are initially organized to treat speech sounds
differently from non-speech, but are also dependent on experience.
Native language reorganizes perceptual sensitivity, selectively maximizing attention to
phonetic features that distinguish native language categories. Newborns can discriminate both
native and non-native phonetic contrasts, but by 6–12 months of age show a decline in
discrimination of many non-native distinctions and an enhancement of sensitivity to native
ones. Changes in perceptual sensitivity during the first year are called ‘functional
reorganization; developing patterns of discrimination in accordance with functional categories
in the native language. One mechanism that underlies functional reorganization might be
statistical; specific properties of input (frequency, distribution) may shape the perceptual
system. When phonetic contrasts are high in frequency, children categorize these quicker.
Infants must learn to recognize and represent contrasting acoustic forms of words.
Word segmentation. Infants begin to segment words by 7–8 months of age. At 7 months,
English-learning infants pull out words that conform to the common English strong-weak
stress pattern, like ‘DOCtor’, but do not segment weakstrong words like ‘guiTAR’, this
happens by 10 months. Once learned, frequent word forms, facilitate segmentation of new
words. Another statistical regularity that infants are sensitive to is ‘transitional probability’,
learning that syllables from within one word are more likely to co-occur than syllables from
separate words.