WEEK 0: PREPRATION BEFORE THE COURSE STARTS (22/08-28/08) ................................................................ 3
Datacamp – Introduction to Python ................................................................................................................... 3
Chapter 1: Python Basics ............................................................................................................................... 3
Chapter 2: Python Lists .................................................................................................................................. 3
Chapter 3: Functions and Packages ............................................................................................................... 4
Table: All Functions from the Chapters ......................................................................................................... 4
WEEK 1 – LECTURE: GETTING STARTED WITH PYTHON & WEB DATA (30/08) .................................................. 6
Lecture Notes ...................................................................................................................................................... 6
Tutorial: Python Bootcamp for Web Data .......................................................................................................... 7
WEEK 2 – TUTORIAL: WEB SCRAPING FOR DUMMIES (08/09) ....................................................................... 11
Video lecture: What is Web Scraping and What are Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)? (20:43) ..... 11
What is web scraping? ................................................................................................................................. 11
What is an API? ............................................................................................................................................ 11
Summary ...................................................................................................................................................... 11
Webinar: Boegershausen, J., Datta, H., Borah, A., & Stephen, A.T. (2022). Fields of Gold: Scraping Web Data
for Marketing Insights. Journal of Marketing, 86(5), 1-20. .............................................................................. 12
Web Data in Academic Marketing Research and How to Extract It............................................................. 12
Pathways for Creating New Marketing Knowledge (terugkijken 6:00) ........................................................ 12
Managing the Idiosyncratic Legal, Technical, and Validity Challenges of Web Data ................................... 12
& Focus on Three Key Stages: Source Selection, Design, Extraction ........................................................... 12
Paper: Boegershausen, J., Datta, H., Borah, A., & Stephen, A.T. (2022). Fields of Gold: Scraping Web Data for
Marketing Insights. Journal of Marketing, 86(5), 1-20. .................................................................................... 13
Abstract........................................................................................................................................................ 13
Introduction ................................................................................................................................................. 13
Using Web Data to Advance Marketing Thought ........................................................................................ 14
§ Studying New Phenomena ........................................................................................................................ 14
§ Boosting Ecological Value ......................................................................................................................... 14
§ Facilitating Methodological Advancement ............................................................................................... 14
§ Improving Measurement .......................................................................................................................... 15
§ Summary ................................................................................................................................................... 15
Methodological Framework for Collecting Web Data ................................................................................. 15
Data Source Selection .................................................................................................................................. 16
Designing the Data Collection ...................................................................................................................... 17
Collecting the Data....................................................................................................................................... 19
Summary tables ........................................................................................................................................... 20
Future Research Opportunities with Web Data........................................................................................... 23
Web Appendix A: Comparing Web Scraping and APIs ................................................................................. 24
Web Appendix C: Marketing Research using Web Data .............................................................................. 25
Web Appendix D: Legal Considerations ....................................................................................................... 25
Web Appendix F: Calculation of Technically Feasible Sample Sizes ............................................................ 25
In-Class Tutorial: Web Data for Dummies ........................................................................................................ 26
After-Class Tutorial: Web Data for Dummies ................................................................................................... 29
WEEK 3 – TUTORIAL: WEB SCRAPING 101 (15/09) ......................................................................................... 40
In-Class Tutorial: Web Scraping 101 ................................................................................................................. 40
, After-Class Tutorial: Web Scraping 101 ............................................................................................................ 41
WEEK 4 – TUTORIAL: APIS 101 (22/09) .......................................................................................................... 54
In-Class Tutorial: APIs 101 ................................................................................................................................ 54
After-Class Exercises: APIs 101 ......................................................................................................................... 56
WEEK 6 – LECTURE: TEAM COACHING #5 (06/10) .......................................................................................... 64
Gebru, T., Morgenstern, J., Vecchione, B., Vaughan, J., Wallach, H., Daumé III, H., & Crawford, K. (2018).
Datasheets for Datasets (cite arxiv:1803.09010). Working paper. .................................................................. 64
1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................................. 64
1.1 Objectives .............................................................................................................................................. 64
3. Questions and Workflow ......................................................................................................................... 64
,WEEK 0: PREPRATION BEFORE THE COURSE STARTS (22/08-28/08)
Literature
Datacamp – Introduction to Python:
• Chapter 1: Python Basics
• Chapter 2: Python Lists
• Chapter 3: Functions and Packages
Datacamp – Introduction to Python
Chapter 1: Python Basics
The Python shell is a place where you can type Python code and immediately see the results. Next to
that, you can also have Python run so called Python scripts. These Python scripts are simply text files
with the extension .py.
Q: For which applications can you use Python?
a. You want to do some quick calculations.
b. For your new business, you want to develop a database-driven website.
c. Your boss asks you to clean and analyze the results of the latest satisfaction survey.
d. All of the above.
A: D.
You can add comments to your Python script by using the # tag.
You can define a variable in Python through the equal-to (=) sign. For example, height = 1.79.
The following data types are common in Python:
• A float is a real number, i.e., a number that has both an integer part and a fractional part (e.g.,
1.1).
• An integer (int) is a number without a fractional part (e.g., 100).
• A string (str) is Python’s way to represent text.
• A Boolean (bool) is a type that can either be True or False.
Q: Which one of these will throw an error?
a. “I can add integers, like ” + str(5) + “ to strings.”
b. “I said ” + (“Hey ” * 2) + “Hey!”
c. The correct answer to this multiple choice exercise is the answer number ” + 2
d. True + False
A: C.
Chapter 2: Python Lists
A list is a compound data type. You can build a list using square brackets. For example, list = [1.73, 1.68,
1.71, 1.89]. A list can contain any Python type. Although it’s not really common, a list can also contain a
mix of Python types including strings, floats, Booleans, etc. A list can also contain a list.
Q: Which of the following lines of Python code are valid ways to build a list?
a. [1, 3, 4, 2]
b. [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 7]]
c. [1 + 2, “a” * 5, 3]
A: A, B, and C.
To select an element from a list, you can use square brackets. For example, fam[2] gives you the second
index – the third item – in the list (Python indexing starts at 0 for the first element in a list). It is also
possible to slice your list, which means selecting multiple elements from your list. For example, fam[3:5]
gives you the third and fourth index – the fourth and fifth elements – of a list, but not the fifth index.
The latter is exclusive.
Q: Remove the poolhouse (the string and float) from the areas list. Which of the code chunks will do
the job for us?
a. del(areas[10]); del(areas[11])
b. del(areas[10:11])
c. del(areas[-4:-2])
d. del(areas[-3]); del(areas[-4])
A: C.
, Chapter 3: Functions and Packages
A function is a piece of reusable code, aimed at solving a particular task. The inputs of functions are
called arguments.
Q: Use the iPython Shell to open up the documentation on pow(). Which of the following statements is
true?
a. pow() takes three arguments: base, exp, and mod. If you don’t specify mod, the function will
return an error.
b. pow() takes three arguments: base, exp, and None. All of these arguments are required.
c. pow() takes three arguments: base, exp, and mod. base and exp are required arguments, mod is
an optional argument.
d. pow() takes two arguments: exp and mod. If you don’t specify exp, the function will return an
error.
A: C.
Values or data structures like strings, floats, and lists are all so-called Python objects. These objects
come with object-specific methods. You can think of methods as functions that “belong to” Python
objects. To call a method, you use the dot notation (see the table below).
A package can be thought of as a directory of Python scripts. Each such script is a so-called module.
These modules specify functions, methods, and new Python types aimed at solving particular problems.
To import a package, you can type import [package]. To use a function from a package, you have to use
the dot notation with the package name in front of it. You can also abbreviate package names to make
coding a bit less time consuming, by using import [package] as [abbreviation]. If you only want to use a
specific part of a package, you can also type from [package] import [function].
Q: Suppose you want to use the function inv(), which is in the linalg subpackage of the scipy package.
You want to be able to use this function as follows: my_inv([[1,2], [3,4]]). Which import statement will
you need in order to run the above code without an error?
a. import scipy
b. import scipy.linalg
c. from scipy.linalg import my_inv
d. from scipy.linalg import inv as my_inv
A: D.
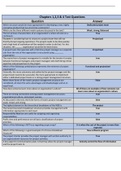
Table: All Functions from the Chapters
Ch. Function Description Example
1 print() Prints what is inside the brackets. print(5+3)
1 type() Check the type of a value. type(bmi)
1 str() Convert a variable to a string. str(savings)
1 int() Convert a variable to an integer. int(savings)
1 float() Convert a variable to a float. float(savings)
1 bool() Convert a variable to a Boolean. bool(savings)
2 del() Delete elements from a list. del(x[1])
2 list() Make a copy of a list. areas_copy = list(areas)
3 max() Find the highest value in a list. max(fam)
3 round() Round a number. round(1.68, 1)
3 help() Get information about a function. help(max) [or: ?max]
3 len() Get the length of a list. len(var1)
3 sorted() Sort a list. full_sorted = sorted(full, reverse = True)
3 index (list) Get the index number from a list fam.index(“mom”)
variable.
3 count (list) Count the number of variables in a fam.count(1.73)
list with a specific value.
3 capitalize Capitalize a string. sister.capitalize()
(str)
3 replace (str) Replace part of a string. sister.replace(“z”, “sa”)
3 index (str) Get the index number from a string sister.index(“z”)
variable.