AIM Slides
College 1
MNE: direct investment in foreign countries, actively manages foreign assets.
Theory of internationalization: Uppsala model
Firm specific advantages
Network centrality
Brokerage
Global strategy: basis means by which the company competes (choice of business and how it
is differentiated from that of its competitors). Needed in global industries in which the
competitive position of a firm at home is affected by its competitive position in a foreign
market.
Home region oriented: over 50% sales in home region
Host region oriented: over 50% sales in host region
Bi-regional: over 20% in each of two regions, less than 50% in one region
Global: over 20% in all markets, less than 50% in one market
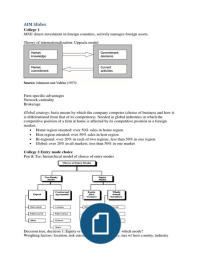
College 2 Entry mode choice
Pan & Tse: hierarchical model of choice of entry modes
Decision tree, decision 1: Equity or non-equity? Decision 2: which mode?
Weighing factors: location, risk orientation, power distance, ties w/ host country, industry
, Contractual agreements (alliance) vs. equity joint ventures
Equity joint venture vs. wholly owned subsidiary = Hennart & Reddy
Greenfield vs. acquisition = Harzing
Firm Assets & Entry Mode Choice
Joint venture vs. Acquisition
-Asset indigestibility -Asset digestible
(Tied/nondesired assets) (Small firm or divisionalized)
-Unclear value of assets -Clear value of assets
(Firm is in different industry) (Firm is in same industry)
Isomorphism: imitation behavior, internal (US firm sticks to US salaries) or external (US firm
pays salary according to host country standards)
Strategy & entry mode choice
Greenfield vs. Acquisition
Global strategy Multidomestic strategy
-Globalization -Local adaption
-Exploitation of -Exploitation of location bound FSA
non-location bound FSA -External isomorphism
-Internal isomorphism
College 3
Clusters: competition & cooperation = co-opetition
Differentiation: brand equity, higher prices, desirable features
Externality
College 1
MNE: direct investment in foreign countries, actively manages foreign assets.
Theory of internationalization: Uppsala model
Firm specific advantages
Network centrality
Brokerage
Global strategy: basis means by which the company competes (choice of business and how it
is differentiated from that of its competitors). Needed in global industries in which the
competitive position of a firm at home is affected by its competitive position in a foreign
market.
Home region oriented: over 50% sales in home region
Host region oriented: over 50% sales in host region
Bi-regional: over 20% in each of two regions, less than 50% in one region
Global: over 20% in all markets, less than 50% in one market
College 2 Entry mode choice
Pan & Tse: hierarchical model of choice of entry modes
Decision tree, decision 1: Equity or non-equity? Decision 2: which mode?
Weighing factors: location, risk orientation, power distance, ties w/ host country, industry
, Contractual agreements (alliance) vs. equity joint ventures
Equity joint venture vs. wholly owned subsidiary = Hennart & Reddy
Greenfield vs. acquisition = Harzing
Firm Assets & Entry Mode Choice
Joint venture vs. Acquisition
-Asset indigestibility -Asset digestible
(Tied/nondesired assets) (Small firm or divisionalized)
-Unclear value of assets -Clear value of assets
(Firm is in different industry) (Firm is in same industry)
Isomorphism: imitation behavior, internal (US firm sticks to US salaries) or external (US firm
pays salary according to host country standards)
Strategy & entry mode choice
Greenfield vs. Acquisition
Global strategy Multidomestic strategy
-Globalization -Local adaption
-Exploitation of -Exploitation of location bound FSA
non-location bound FSA -External isomorphism
-Internal isomorphism
College 3
Clusters: competition & cooperation = co-opetition
Differentiation: brand equity, higher prices, desirable features
Externality