Coulomb’s Law
The forces between 2 charged particles 𝒒𝟏 and 𝒒𝟐 separated by distance 𝒓 are :
𝐾|𝑞1 ||𝑞2 |
𝐹1 𝑜𝑛 2 = 𝐹2 𝑜𝑛 1 =
𝑟2
1
Where 𝐾 = is called the electrostatic constant
4𝜋𝜀0
- Coulomb’s law applies only to point charges
- Electric forces, like other forces, can be superimposed
- The forces are repulsive for 2 like charges, attractive for 2 opposite charges
The Charge Model
There are two kinds of charge, positive and negative :
- Fundamental charges are protons and electrons, with charge ±𝑒 with 𝑒 being the
fundamental unit of charge (𝑒 = 1.60 ∙ 10−19 𝐶)
- Objects are charged by adding or removing electrons
→ Charge varies by discrete steps , not continuously (=charge quantization)
- The amount of charge is 𝑞 = (𝑁𝑝 − 𝑁𝑒 )𝑒
- A neutral object has no charge
- Charge is neither created nor destroyed (=law of conservation of charge)
There are two types of material, insulators and conductors :
- Charge remains fixed in or on an insulator
- Charge moves easily through or along conductors
- Charge is transferred by contact between objects
NOTE Both insulators and conductors can be charged, they differ in the mobility of the charge
Charged objects attract neutral objects :
- Charge polarizes metal by shifting the electron sea
- Charge polarizes atoms, creating electric dipoles
- The polarization force is always an attractive force
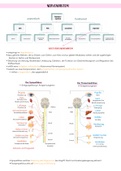
,The Electroscope
The process by which an electroscope is charged :
The Field Model
Charges interact with each other via the electric field 𝐸⃗ :
- Charges alter the space around themselves by creating an electric field
- The field is the agent that exerts a force
An electric field is identified and measured in terms of the force on a positive probe charge 𝑞 :
𝐹𝑜𝑛 𝑞
𝐸⃗ =
𝑞
- The electric field exists at all points in space
- An electric field vector shows the field only at one point, the point at the tail of the vector
,Chapter 23 : The Electric Field
Point Charge (with charge 𝑞)
The force that a point charge 𝑞 exerts on a probe charge 𝑞′ is equal to
1 𝑞𝑞′
𝐹⃗𝑜𝑛 𝑞′ = ( , 𝑎𝑤𝑎𝑦 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑞)
4𝜋𝜀0 𝑟 2
The electric field of the source charge 𝑞 is then equal to
𝐹⃗𝑜𝑛 𝑞′ 1 𝑞
𝐸⃗⃗ = = 𝑟̂
𝑞′ 4𝜋𝜀0 𝑟 2
𝐶2
With 𝑟̂ being a vector unit pointing away from source charge 𝑞 and 𝜀0 = 8,55 ∙ 10−12 𝑁𝑚2
Multiple charges
Electric fields obey the principle of superposition
Limiting cases
(𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑡 )𝑧 = 0 → in the 𝑥𝑦-plane
(𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑡 )𝑦 = 0 → 𝐸1 and 𝐸3 have equal magnitudes and tilted with same angle 𝜃
(𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑡 )𝑥 = (𝐸1 )𝑥 + (𝐸2 )𝑥 + (𝐸3 )𝑥 = 2(𝐸1 )𝑥 + (𝐸2 )𝑥
1 𝑞2 1 𝑞
(𝐸2 )𝑥 = 𝐸2 = 2 = (𝑟2 = 𝑥)
4𝜋𝜀0 𝑟2 4𝜋𝜀0 𝑥 2
1 𝑞1
(𝐸1 )𝑥 = 𝐸1 cos 𝜃 = cos 𝜃
4𝜋𝜀0 𝑟12
𝑟1 and 𝜃 both vary with position 𝑥 𝑥
𝑥, they need to be expressed in Pythagorean Theorem : 𝑟1 = √𝑥 2 + 𝑑 2 cos 𝜃 = =
𝑟1 √𝑥 2 + 𝑑 2
function of 𝑥
1 𝑞 𝑥 1 𝑥𝑞
(𝐸1 )𝑥 = =
4𝜋𝜀0 𝑥 + 𝑑 √𝑥 2 + 𝑑2 4𝜋𝜀0 (𝑥 2 + 𝑑2 )32
2 2
𝑞 1 2𝑥
(𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑡 )𝑥 = 2(𝐸1 )𝑥 + (𝐸2 )𝑥 = ( 2+ 3)
4𝜋𝜀0 𝑥 (𝑥 2 + 𝑑2 )2
𝑞 1 2𝑥
𝐸⃗⃗𝑛𝑒𝑡 = ( 2+ 3) î
4𝜋𝜀0 𝑥 (𝑥 2 + 𝑑2 )2
, 2 cases :
- 𝑥 ≪ 𝑑 (𝑥 → 0)
Becomes a single point charge 𝑞 at the origin (𝐸⃗⃗1 and 𝐸⃗⃗3 become opposite and cancel)
2𝑥
lim 3 =0 (approximating 0)
𝑥→0 (𝑥 2 +𝑑2 )2
1 𝑞
→ 𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑡 = 4𝜋𝜀 𝑥2
= Field of single point charge
0
1
In no 𝑑, thus no approximation
𝑥2
- 𝑥 ≫ 𝑑 (𝑥 → ∞)
The field is zero in the limit 𝑥 → ∞. Doesn’t tell much, 𝑥 just has to be very large in
comparison to the spacing 𝑑 between the source charges.
Then the denominator of the second term is well approximated by :
3 3
(𝑥 2 + 𝑑2 )2 ≈ (𝑥 2 )2 = 𝑥 3
1 2𝑥 1 2𝑥 3
Thus, lim (𝑥 2 + 3 ) = 𝑥2 + 𝑥3 = 𝑥2
𝑥≫𝑑 (𝑥 2 +𝑑 2 )2
1 3𝑞
𝐸⃗⃗𝑛𝑒𝑡 = 4𝜋𝜀 î this is the electric field op a point charge 3𝑞
0 𝑥2
Dipole
Two equal but opposite charges ±𝑞 separated by a small distance 𝑠 form an electric dipole :
- Permanent electric dipole (ex. water molecule)
- Induced electric dipole (polarizing a neutral atom with an external electric field)
(𝐸𝑑𝑖𝑝𝑜𝑙𝑒 )𝑦 = (𝐸+ )𝑦 + (𝐸− )𝑦
1 𝑞 1 (−𝑞)
= 2 +
4𝜋𝜀0 1 4𝜋𝜀0 1 2
(𝑦 − 2 𝑠) (𝑦 + 2 𝑠)
𝑞 1 1
= ( 2 − )
4𝜋𝜀0 1 1 2
(𝑦 − 2 𝑠) (𝑦 + 2 𝑠)
𝑞 2𝑦𝑠
(𝐸𝑑𝑖𝑝𝑜𝑙𝑒 )𝑦 = ( )
4𝜋𝜀0 1 2 1 2
(𝑦 − 2 𝑠) (𝑦 + 2 𝑠)
In practice, electric field of a dipole always observed at distances 𝑦 ≫ 𝑠, distances much larger
than the charge separation.
1 2 1 2
Denominator can be approximated (𝑦 − 2 𝑠) (𝑦 + 2 𝑠) ≈ 𝑦 4
1 2𝑞𝑠
(𝐸𝑑𝑖𝑝𝑜𝑙𝑒 )𝑦 ≈
4𝜋𝜀0 𝑦 3