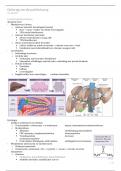
CH 16
1. blood
- a transporter
- a buffer/ protector
- circulating portion of the ECF: extracellulair vocht: in weefsels tussen cellen en bloed
- a medium for thermoregulation: huid: vasodilatatie (bloedvaten wijder worden; meer
bloed; warm bloed naar buitenkant gebracht; warmte transfer met omgeving)
- 7% of total body weight (5L)
- 3L plasma
- 2L cellular elements
plasma proteins
= create osmotic pressure gradient; absorption of H2O
= transport; blood clotting; defense; carriers; hormones
- hoe meer proteïne, hoe meer water aantrekken; hoe groter volume
2. plasma
- water is the main component 92%
- proteines 7%
- 1% dissolved organics molecules (Ca2+;...)
- albumines: most prevalent type of protein in the plasma (60%)
- 90%: to globuline; fibrinogen (clotting protein); transferrine (iron transporting protein)
- liver: makes most plasma and secretes it into the blood
- some globuline; as immunoglobulins or antibodies: synthesized and secretes-d by
specialized blood cells rather than the liver
- presence of proteins in plasma → osmotic pressure of blood higher than interstitial
fluid
- osmotic gradient: pulls water from interstitial fluid into capillaries and offset filtration
out of the capillaries created by blood pressure
- FUNCTIE plasma protein: blood clotting; defense against foreign invaders, act as
carriers for steroid hormones; cholesterol; drugs; hormones; enzymes
Albumine Globuline Immunoglobulines Fibrinogen Transferrin
*most prevalent *different types IgA: *thrombin *control the
plasma protein and sizes (alpha - found in converts level of iron
(60%) 1&2; beta; external fibrinogen in
gamma) secretions fibrin
(mucus)
- binds to
pathogens
- flags them
for
phagocytosis
if they reach
internal
environment
,*maintaining *gamma: IgD: *essential for *important
osmotic immunoglobulin - antibody blood transporter for
pressure in s or antibodies protein that clotting: iron
vessels appears on bridges
the surface between
of B platelets
lymphocytes
- physiological
role unclear
*transporter *immunoglobuli IgE: *high levels
(ions; nes: - target gut associated
hormones; - identify parasites with
medication) and - associated cardiovascul
neutraliz with allergic ar disease or
e reactions inflammation
bacteria
and
viruses
- antibody
recogniz
es an
antigen
- the tip of
each
antibody
is
specific
for an
antigen
(key
lock)
*high albumin in IgG: *low levels:
blood - 75% of pathological
(hyperalbumine plasma activation of
mia) → water antibody in coagulation;
drawn into adults leads to
blood - produced in excessive
(dehydration) secondary use of
immune fibrinogen →
response blood clots
- can cross the
placental Coagulatie:
membrane; Coagulatie is
giving infants het proces
immunity waarbij een
vloeistof of
een
oplossing
verandert in
een vaste of
halfvaste
massa;
, bloed stolt
om
bloedverlies
te stoppen.
Wanneer
een bloedvat
beschadigd
is, worden
bloedplaatjes
en eiwitten
zoals
fibrinogeen
geactiveerd
en vormen
ze een
stolsel dat de
wond afdicht.
*low albumin: IgM:
hypoalbuminemi - biggest en
a (liver disease; heaviest
malnutrition) - primary
immune
response
*antigeen bindt op
antilichaam: meer
gevormd; leven niet
lang
(geheugencellen:
aantal blijven in
leven; lange tijd in
lichaam blijven)
3. cellular elements
- red blood cells → erythrocytes; lost nuclei; transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide
- platelets → split off from megakaryocytes → thrombocytes; no nuclei; coagulatie
- white blood cells →leukocytes; immune response: defending against foreign invaders
➔ lymphocytes: immunocytes; specific immune response
➔ monocytes; develop into macrophages → phagocytes
➔ neutrophils: phagocytes and granulocytes; immune response
➔ eosinophils: granulocytes; destroy parasites
➔ basophils: granulocytes: allergic reactions → mast cells
phagocytes: engulf and ingest foreign particles
granulocytes: contain cytoplasmic inclusions that give granular appearance
4. hematopoiesis
= aanmaak nieuwe bloedcellen; duurt tot je sterft (gedurende leven nieuwe cellen
aanmaken)
- begins in embryonic phase
1. blood
- a transporter
- a buffer/ protector
- circulating portion of the ECF: extracellulair vocht: in weefsels tussen cellen en bloed
- a medium for thermoregulation: huid: vasodilatatie (bloedvaten wijder worden; meer
bloed; warm bloed naar buitenkant gebracht; warmte transfer met omgeving)
- 7% of total body weight (5L)
- 3L plasma
- 2L cellular elements
plasma proteins
= create osmotic pressure gradient; absorption of H2O
= transport; blood clotting; defense; carriers; hormones
- hoe meer proteïne, hoe meer water aantrekken; hoe groter volume
2. plasma
- water is the main component 92%
- proteines 7%
- 1% dissolved organics molecules (Ca2+;...)
- albumines: most prevalent type of protein in the plasma (60%)
- 90%: to globuline; fibrinogen (clotting protein); transferrine (iron transporting protein)
- liver: makes most plasma and secretes it into the blood
- some globuline; as immunoglobulins or antibodies: synthesized and secretes-d by
specialized blood cells rather than the liver
- presence of proteins in plasma → osmotic pressure of blood higher than interstitial
fluid
- osmotic gradient: pulls water from interstitial fluid into capillaries and offset filtration
out of the capillaries created by blood pressure
- FUNCTIE plasma protein: blood clotting; defense against foreign invaders, act as
carriers for steroid hormones; cholesterol; drugs; hormones; enzymes
Albumine Globuline Immunoglobulines Fibrinogen Transferrin
*most prevalent *different types IgA: *thrombin *control the
plasma protein and sizes (alpha - found in converts level of iron
(60%) 1&2; beta; external fibrinogen in
gamma) secretions fibrin
(mucus)
- binds to
pathogens
- flags them
for
phagocytosis
if they reach
internal
environment
,*maintaining *gamma: IgD: *essential for *important
osmotic immunoglobulin - antibody blood transporter for
pressure in s or antibodies protein that clotting: iron
vessels appears on bridges
the surface between
of B platelets
lymphocytes
- physiological
role unclear
*transporter *immunoglobuli IgE: *high levels
(ions; nes: - target gut associated
hormones; - identify parasites with
medication) and - associated cardiovascul
neutraliz with allergic ar disease or
e reactions inflammation
bacteria
and
viruses
- antibody
recogniz
es an
antigen
- the tip of
each
antibody
is
specific
for an
antigen
(key
lock)
*high albumin in IgG: *low levels:
blood - 75% of pathological
(hyperalbumine plasma activation of
mia) → water antibody in coagulation;
drawn into adults leads to
blood - produced in excessive
(dehydration) secondary use of
immune fibrinogen →
response blood clots
- can cross the
placental Coagulatie:
membrane; Coagulatie is
giving infants het proces
immunity waarbij een
vloeistof of
een
oplossing
verandert in
een vaste of
halfvaste
massa;
, bloed stolt
om
bloedverlies
te stoppen.
Wanneer
een bloedvat
beschadigd
is, worden
bloedplaatjes
en eiwitten
zoals
fibrinogeen
geactiveerd
en vormen
ze een
stolsel dat de
wond afdicht.
*low albumin: IgM:
hypoalbuminemi - biggest en
a (liver disease; heaviest
malnutrition) - primary
immune
response
*antigeen bindt op
antilichaam: meer
gevormd; leven niet
lang
(geheugencellen:
aantal blijven in
leven; lange tijd in
lichaam blijven)
3. cellular elements
- red blood cells → erythrocytes; lost nuclei; transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide
- platelets → split off from megakaryocytes → thrombocytes; no nuclei; coagulatie
- white blood cells →leukocytes; immune response: defending against foreign invaders
➔ lymphocytes: immunocytes; specific immune response
➔ monocytes; develop into macrophages → phagocytes
➔ neutrophils: phagocytes and granulocytes; immune response
➔ eosinophils: granulocytes; destroy parasites
➔ basophils: granulocytes: allergic reactions → mast cells
phagocytes: engulf and ingest foreign particles
granulocytes: contain cytoplasmic inclusions that give granular appearance
4. hematopoiesis
= aanmaak nieuwe bloedcellen; duurt tot je sterft (gedurende leven nieuwe cellen
aanmaken)
- begins in embryonic phase