Cellular Respiration - A Guide
Glycolysis:
● Glycolysis is an anaerobic process that occurs in the cytosol and breaks down
glucose (6C) into two molecules of pyruvate (3C).
● Glycolysis I involves the phosphorylation of glucose using ATP.
● Glycolysis II involves the production of ATP and NADH through a series of
reactions, including oxidation, phosphorylation, and removal of water.
Pyruvate Oxidation:
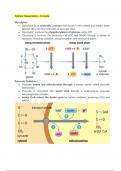
● Pyruvate enters the mitochondria through a protein carrier called pyruvate
translocase.
● Pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA through a multi-enzyme pyruvate
dehydrogenase complex.
● Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle for further oxidation, producing CO2 and
NADH.
, Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle):
● The Krebs cycle is a cyclic metabolic pathway that occurs in the mitochondrial
matrix.
● Acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate to produce citrate, which undergoes
a series of reactions, including isomerization, oxidation/reduction,
decarboxylation, and substrate-level phosphorylation.
● The net production for each molecule of acetyl-CoA is 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1
ATP. The Krebs cycle turns twice for every molecule of glucose.
Glycolysis:
● Glycolysis is an anaerobic process that occurs in the cytosol and breaks down
glucose (6C) into two molecules of pyruvate (3C).
● Glycolysis I involves the phosphorylation of glucose using ATP.
● Glycolysis II involves the production of ATP and NADH through a series of
reactions, including oxidation, phosphorylation, and removal of water.
Pyruvate Oxidation:
● Pyruvate enters the mitochondria through a protein carrier called pyruvate
translocase.
● Pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA through a multi-enzyme pyruvate
dehydrogenase complex.
● Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle for further oxidation, producing CO2 and
NADH.
, Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle):
● The Krebs cycle is a cyclic metabolic pathway that occurs in the mitochondrial
matrix.
● Acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate to produce citrate, which undergoes
a series of reactions, including isomerization, oxidation/reduction,
decarboxylation, and substrate-level phosphorylation.
● The net production for each molecule of acetyl-CoA is 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1
ATP. The Krebs cycle turns twice for every molecule of glucose.