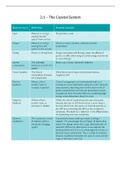
EVOLUTION
Background info
- Universe started 13.7 bya
(billion years ago)
- Dating of fossils include
relative dating and
radiometric/absolute
dating
- There has been at least 5
mass extinctions
- By studying fossils one
can learn about ancient
forms, understand that
life-forms changed and
gradually became more
similar to present-day
life-forms and it gains
evidence to support the
idea that species change
- SA is very rich in fossils
with some important finds
such as:
1. Earliest organisms
(3.5bya) like the
Stromatolites
2. Primitive land plants such
as the fern
3. The Coelacanth (fish
group ancestral to
amphibians)
4. Mammal-like reptiles (a
bridge between reptiles
and mammals)
5. Austalopithicus Africanus
and Homo Ergaster
,Development of the theory of evolution
What evolution is
- The change in DNA in an organism over time by mutations
- Gradual change or development
What biological evolution is
- The change in the gene pool of a population during the course of time by
processes such as mutations, natural selection and genetic drift
- Basically is descent with modification
- Population = the same species close enough to produce fertile offspring
- Bigger gene pool = more variation
Micro-evolution = evolution within a species (allele changes)
Macroevolution = the descent of different species from a common ancestor over many
generations (gene changes)
Descent with modification = Charles Darwin -> selective pressures
Speciation = forming a few species
Palaeontology -> studying fossils
Pentadactyl limb = homologous limb
Importance of biological evolution
Biological evolution:
1. Has become the unifying concept that acts as a foundation for understanding all
biology
2. Supports and explains many aspects of our everyday life
3. Challenges people to really think for themselves
How life originated
- Current scientific opinion us that there was a single origin of life
How species diversity originated
BEFORE 1700 SCIENTISTS ACCEPTED:
- Species were unrelated and remained unchanged
- Earth was young and static (unchanging)
,1700 TO EARLY 1800
- Erasmus Darwin (Charles’s grandfather) and Jean-Baptiste Lemarck began to
challenge these concepts
- They became convinced that species has changed gradually over time and the
earth was millions of years old
Erasmus Darwin
- Successful doctor, scientist, philosopher, inventor
- Famous book, Zoonomia, put forward the idea that life on earth descended from
a common ancestor
- It also suggested that species must have changed over time but offered no
mechanism for what he termed ‘transformation’ (evolution)
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
- French naturalist
- Around a decade later, he put forward his ideas on evolution in his book,
Philosophie Zoologique, and also proposed that species were not fixed
- Reached this conclusion as a result of making various observations like:
1. Living species are different to fossil types
2. Domestication and selective breeding resulted in animals and plants changing
3. Cross-breeding of plant species often led to new characters appearing
HOW LAMARCK SUGGESTED THIS
- He proposed that change was a natural phenomenon and not a result of divine
intervention
- Suggested organisms changed during their lifetime so they could survive in new
environments
- And these acquired changes were then passed onto offspring
1. Use and disuse of body parts
- Believed that when environment changed, the organism would actively
respond by changing so it could adapt to new environment
2. Inheritance of acquired characteristics
- Physical (phenotypes) changes acquired by parents during their lifetime
were passed on to their offspring which is how new species were formed
, Example:
- Suggested long neck and
legs of modern giraffes
were result of
generations of
short-necked and
short-legged ancestors
stretching their necks to
feed on leaves at
progressively higher
levels
- Thought that acquired
characteristics (longer
legs and necks) were passed onto offspring of each generation until eventually a
new species of giraffe with very long legs and necks appeared
Was Lamarck correct?
- Lamarck's belief that environment can produce phenotypic changes in an
individual was correct
- He was incorrect in thinking this caused evolutionary change
- Eg. bodybuilding will increase muscle size, however this does not alter the
genotype of gametes, therefore cannot be passed onto offspring
EARLY 1800 TO EARLY 1900
- Charles Darwin and Alred Russel Wallace
Charles Darwin
- Began formulating theories after 5 year expedition to southern hemisphere where
he studied, observed and documented info
His info he collected made him aware of the:
1. Immense diversity among organisms both living and extinct
2. Variation of individuals of the same species, suggesting species were not
unchangeable
3. Often puzzling distribution of different species
Background info
- Universe started 13.7 bya
(billion years ago)
- Dating of fossils include
relative dating and
radiometric/absolute
dating
- There has been at least 5
mass extinctions
- By studying fossils one
can learn about ancient
forms, understand that
life-forms changed and
gradually became more
similar to present-day
life-forms and it gains
evidence to support the
idea that species change
- SA is very rich in fossils
with some important finds
such as:
1. Earliest organisms
(3.5bya) like the
Stromatolites
2. Primitive land plants such
as the fern
3. The Coelacanth (fish
group ancestral to
amphibians)
4. Mammal-like reptiles (a
bridge between reptiles
and mammals)
5. Austalopithicus Africanus
and Homo Ergaster
,Development of the theory of evolution
What evolution is
- The change in DNA in an organism over time by mutations
- Gradual change or development
What biological evolution is
- The change in the gene pool of a population during the course of time by
processes such as mutations, natural selection and genetic drift
- Basically is descent with modification
- Population = the same species close enough to produce fertile offspring
- Bigger gene pool = more variation
Micro-evolution = evolution within a species (allele changes)
Macroevolution = the descent of different species from a common ancestor over many
generations (gene changes)
Descent with modification = Charles Darwin -> selective pressures
Speciation = forming a few species
Palaeontology -> studying fossils
Pentadactyl limb = homologous limb
Importance of biological evolution
Biological evolution:
1. Has become the unifying concept that acts as a foundation for understanding all
biology
2. Supports and explains many aspects of our everyday life
3. Challenges people to really think for themselves
How life originated
- Current scientific opinion us that there was a single origin of life
How species diversity originated
BEFORE 1700 SCIENTISTS ACCEPTED:
- Species were unrelated and remained unchanged
- Earth was young and static (unchanging)
,1700 TO EARLY 1800
- Erasmus Darwin (Charles’s grandfather) and Jean-Baptiste Lemarck began to
challenge these concepts
- They became convinced that species has changed gradually over time and the
earth was millions of years old
Erasmus Darwin
- Successful doctor, scientist, philosopher, inventor
- Famous book, Zoonomia, put forward the idea that life on earth descended from
a common ancestor
- It also suggested that species must have changed over time but offered no
mechanism for what he termed ‘transformation’ (evolution)
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
- French naturalist
- Around a decade later, he put forward his ideas on evolution in his book,
Philosophie Zoologique, and also proposed that species were not fixed
- Reached this conclusion as a result of making various observations like:
1. Living species are different to fossil types
2. Domestication and selective breeding resulted in animals and plants changing
3. Cross-breeding of plant species often led to new characters appearing
HOW LAMARCK SUGGESTED THIS
- He proposed that change was a natural phenomenon and not a result of divine
intervention
- Suggested organisms changed during their lifetime so they could survive in new
environments
- And these acquired changes were then passed onto offspring
1. Use and disuse of body parts
- Believed that when environment changed, the organism would actively
respond by changing so it could adapt to new environment
2. Inheritance of acquired characteristics
- Physical (phenotypes) changes acquired by parents during their lifetime
were passed on to their offspring which is how new species were formed
, Example:
- Suggested long neck and
legs of modern giraffes
were result of
generations of
short-necked and
short-legged ancestors
stretching their necks to
feed on leaves at
progressively higher
levels
- Thought that acquired
characteristics (longer
legs and necks) were passed onto offspring of each generation until eventually a
new species of giraffe with very long legs and necks appeared
Was Lamarck correct?
- Lamarck's belief that environment can produce phenotypic changes in an
individual was correct
- He was incorrect in thinking this caused evolutionary change
- Eg. bodybuilding will increase muscle size, however this does not alter the
genotype of gametes, therefore cannot be passed onto offspring
EARLY 1800 TO EARLY 1900
- Charles Darwin and Alred Russel Wallace
Charles Darwin
- Began formulating theories after 5 year expedition to southern hemisphere where
he studied, observed and documented info
His info he collected made him aware of the:
1. Immense diversity among organisms both living and extinct
2. Variation of individuals of the same species, suggesting species were not
unchangeable
3. Often puzzling distribution of different species