Human Reproduction
Gametes have the haploid (n) chromosome number.
Two haploid gametes (1 sperm and 1 ovum) fuse during fertilisation to form a diploid (2n) zygote.
The zygote develops into a multicellular diploid (2n) organism.
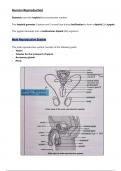
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of the following parts:
- Testes
- Tubules for the transport of sperm
- Accessory glands
- Penis
,Testes
The primary male sex organs are the pair of testes.
The temperature of the testes is 2 - 3°C lower than the body temperature, ensuring optimal
sperm production.
The testis is an oval-shaped gland, about 5 cm in length and it is externally enclosed by a sac of
skin, the scrotum.
Internally the testis is divided into small
lobules. Each lobule contains several
closely packed, convoluted seminiferous
tubules (up to 500m long).
The seminiferous tubules are lined with
special cells, called germinal epithelium.
These germinal epithelium cells divide
and give rise to sperm (male gametes), in a process known as spermatogenesis.
A few of the germinal epithelium cells
develop into large columnar cells,
known as the Sertoli cells. These cells
provide food for the developing sperm.
The seminiferous tubules are
surrounded by connective tissue,
containing groups of interstitial cells
known as cells of Leydig. These cells
produce the male hormone,
testosterone.
Functions of the testes
The testes produce and release sperm (spermatozoa).
It produces the male sex hormone, testosterone, that is responsible for the development of the
secondary sexual characteristics.
,Tubules for the transport of sperm
Epididymis
The seminiferous tubules join to form the epididymis, a long convoluted tubule (5cm in length).
These tubules are situated at the back of the testes and are lined with a mucous membrane.
Functions of the epididymis
The epididymis stores sperm that is produced in the testes. The sperm mature in the epididymis
until they are ready to fertilise the ovum.
The mucous membrane lining the epididymis secretes a substance that, together with the
peristaltic movements of the tubule walls, facilitate the movement of the sperm.
Vas deferens (Sperm duct)
The vas deferens (sperm duct) is a continuation of the epididymis, which passes through the
abdominal cavity and opens in the urethra.
Function of the vas deferens
The vas deferens transports sperm, by means of peristaltic movements, from the epididymis to
the urethra.
Ejaculatory duct
The vas deferens leads to a muscular tubule, the ejaculatory duct.
Function of the ejaculatory duct
The smooth muscle fibres in the duct wall contract, forcing the contents of the duct (semen)
along the urethra to the exterior. (Ejaculation - the release of sperm)
Urethra
The two ejaculatory ducts join the urethra, which opens to the exterior.
Function of the urethra
The urethra transports both urine and sperm (in semen) to the exterior, without passing through
at the same time.
, Accessory glands
Seminal vesicles
The seminal vesicles are two sac-like structures lined with a mucous membrane that secretes a
yellowish, sticky substance.
Function of the seminal vesicle
The secretion of the mucous membrane provides fructose, the main source of food for the
sperm.
Prostate gland
The prostate gland is situated against the bladder and secretes a milky alkaline liquid, the
prostate fluid, which gives semen its characteristic smell.
Functions of the prostate gland
It secretes prostate fluid that:
- ensures maximum motility of sperm.
- protects sperm against the low pH in the urethra and vagina.
(Circumcision - surgical removal of foreskin)
Penis
The penis is the male sex organ.
It consists of a shaft and a head region.
The shaft is divided into 3 columns of erectile tissue:
- Corpus cavernosa (corpus cavernosum): 2 columns that form the upper part of the penis.
- Corpus spongiosum: 1 smaller column that surrounds the urethra on the lower part of the
penis. The spongy tissue ensures that the urethra remains open during an erection for the
passage of semen.
Erectile tissue in these columns becomes filled with blood during arousal due to increased
blood pressure and blood flow. This causes an erection which allows the firm penis to be
inserted in the vagina to release sperm near the cervix.
Gametes have the haploid (n) chromosome number.
Two haploid gametes (1 sperm and 1 ovum) fuse during fertilisation to form a diploid (2n) zygote.
The zygote develops into a multicellular diploid (2n) organism.
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of the following parts:
- Testes
- Tubules for the transport of sperm
- Accessory glands
- Penis
,Testes
The primary male sex organs are the pair of testes.
The temperature of the testes is 2 - 3°C lower than the body temperature, ensuring optimal
sperm production.
The testis is an oval-shaped gland, about 5 cm in length and it is externally enclosed by a sac of
skin, the scrotum.
Internally the testis is divided into small
lobules. Each lobule contains several
closely packed, convoluted seminiferous
tubules (up to 500m long).
The seminiferous tubules are lined with
special cells, called germinal epithelium.
These germinal epithelium cells divide
and give rise to sperm (male gametes), in a process known as spermatogenesis.
A few of the germinal epithelium cells
develop into large columnar cells,
known as the Sertoli cells. These cells
provide food for the developing sperm.
The seminiferous tubules are
surrounded by connective tissue,
containing groups of interstitial cells
known as cells of Leydig. These cells
produce the male hormone,
testosterone.
Functions of the testes
The testes produce and release sperm (spermatozoa).
It produces the male sex hormone, testosterone, that is responsible for the development of the
secondary sexual characteristics.
,Tubules for the transport of sperm
Epididymis
The seminiferous tubules join to form the epididymis, a long convoluted tubule (5cm in length).
These tubules are situated at the back of the testes and are lined with a mucous membrane.
Functions of the epididymis
The epididymis stores sperm that is produced in the testes. The sperm mature in the epididymis
until they are ready to fertilise the ovum.
The mucous membrane lining the epididymis secretes a substance that, together with the
peristaltic movements of the tubule walls, facilitate the movement of the sperm.
Vas deferens (Sperm duct)
The vas deferens (sperm duct) is a continuation of the epididymis, which passes through the
abdominal cavity and opens in the urethra.
Function of the vas deferens
The vas deferens transports sperm, by means of peristaltic movements, from the epididymis to
the urethra.
Ejaculatory duct
The vas deferens leads to a muscular tubule, the ejaculatory duct.
Function of the ejaculatory duct
The smooth muscle fibres in the duct wall contract, forcing the contents of the duct (semen)
along the urethra to the exterior. (Ejaculation - the release of sperm)
Urethra
The two ejaculatory ducts join the urethra, which opens to the exterior.
Function of the urethra
The urethra transports both urine and sperm (in semen) to the exterior, without passing through
at the same time.
, Accessory glands
Seminal vesicles
The seminal vesicles are two sac-like structures lined with a mucous membrane that secretes a
yellowish, sticky substance.
Function of the seminal vesicle
The secretion of the mucous membrane provides fructose, the main source of food for the
sperm.
Prostate gland
The prostate gland is situated against the bladder and secretes a milky alkaline liquid, the
prostate fluid, which gives semen its characteristic smell.
Functions of the prostate gland
It secretes prostate fluid that:
- ensures maximum motility of sperm.
- protects sperm against the low pH in the urethra and vagina.
(Circumcision - surgical removal of foreskin)
Penis
The penis is the male sex organ.
It consists of a shaft and a head region.
The shaft is divided into 3 columns of erectile tissue:
- Corpus cavernosa (corpus cavernosum): 2 columns that form the upper part of the penis.
- Corpus spongiosum: 1 smaller column that surrounds the urethra on the lower part of the
penis. The spongy tissue ensures that the urethra remains open during an erection for the
passage of semen.
Erectile tissue in these columns becomes filled with blood during arousal due to increased
blood pressure and blood flow. This causes an erection which allows the firm penis to be
inserted in the vagina to release sperm near the cervix.