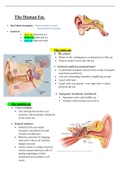
The Human Ear.
➢ Has 2 kinds of receptors: - Those sensitive to sound.
- Those sensitive to gravity.
➢ Consist of:
• Outer ear {filled with air}
• Middle ear {filled with air}
• Inner ear {filled with fluid}
- The outer ear
➢ The pinna:
• Refers to the cartilaginous, external part of the ear.
• Directs sound waves into the ear.
➢ External auditory meatus/canal:
• A canal that channels sound waves to the Tympanic
membrane {eardrum}
• Acts as a resonating chamber, amplifying sound.
• Lined with hair.
• Lined with wax glands - wax traps dirt = which
protects the ear.
➢ Tympanic membrane {eardrum}:
• Separates outer and middle ear.
• Vibrates when sound waves hit it.
- The middle ear
➢ Oval window:
• The stirrups fit into the oval
window, and transmits vibrations
to the inner ear.
➢ Round window:
• Sealed by the secondary
tympanic membrane {round
window membrane}
• Releases pressure by bulging
outwards when oval window
bulges inwards
• Allows fluid in cochlea to move,
which ensures that hair cells of
basilar membrane will be
stimulated and audition will
occur.
, - The middle ear continuation.
➢ Eustachian tube:
• Air-filled canal connecting the middle ear with the
pharynx.
• Controls the pressure within the middle ear,
making it equal with the air pressure outside the
body so that the eardrum vibrates effectively.
➢ Ossicles:
• Refer to 3 tiny bones in the ear {hammer; anvil; stirrup}
• The hammer contract with the eardrum and anvil, the stirrup is in contact with
the anvil and oval window.
• The ossicles are connected via joints and held by ligaments.
• Vibrations are picked up by the ossicles and transmitted to the oval window.
• Amplified vibrations from the eardrum are reduced by the ossicles so the inner
ear is not damaged.
- The inner ear
➢ Bony & membranous labyrinth:
• Bony labyrinth refers to cavities inside the
temporal bone.
• Within the bony labyrinth is the
membranous labyrinth.
• Between the 2 is a fluid called Perilymph.
• Fluid inside the membranous labyrinth is
called Endolymph.
➢ Semi-circular canals:
• 3 canals all perpendicular to each other.
• At end of each canal are ampullae.
• Inside the ampullae are cristae ampullaris, the
- Cochlea= hearing. sense organ of rotation.
- Canals = head movements. • The function of the ampulla is to detect change
- Vestibule= gravity. in direction of head, aand other head
movements
➢ Vestibule:
• Consist of the Utriculus & Sacculus.
• Within the utriculus & the Sacculus are macula.
• The macula contains receptors for changes in position of head with respect
to gravity.
➢ Has 2 kinds of receptors: - Those sensitive to sound.
- Those sensitive to gravity.
➢ Consist of:
• Outer ear {filled with air}
• Middle ear {filled with air}
• Inner ear {filled with fluid}
- The outer ear
➢ The pinna:
• Refers to the cartilaginous, external part of the ear.
• Directs sound waves into the ear.
➢ External auditory meatus/canal:
• A canal that channels sound waves to the Tympanic
membrane {eardrum}
• Acts as a resonating chamber, amplifying sound.
• Lined with hair.
• Lined with wax glands - wax traps dirt = which
protects the ear.
➢ Tympanic membrane {eardrum}:
• Separates outer and middle ear.
• Vibrates when sound waves hit it.
- The middle ear
➢ Oval window:
• The stirrups fit into the oval
window, and transmits vibrations
to the inner ear.
➢ Round window:
• Sealed by the secondary
tympanic membrane {round
window membrane}
• Releases pressure by bulging
outwards when oval window
bulges inwards
• Allows fluid in cochlea to move,
which ensures that hair cells of
basilar membrane will be
stimulated and audition will
occur.
, - The middle ear continuation.
➢ Eustachian tube:
• Air-filled canal connecting the middle ear with the
pharynx.
• Controls the pressure within the middle ear,
making it equal with the air pressure outside the
body so that the eardrum vibrates effectively.
➢ Ossicles:
• Refer to 3 tiny bones in the ear {hammer; anvil; stirrup}
• The hammer contract with the eardrum and anvil, the stirrup is in contact with
the anvil and oval window.
• The ossicles are connected via joints and held by ligaments.
• Vibrations are picked up by the ossicles and transmitted to the oval window.
• Amplified vibrations from the eardrum are reduced by the ossicles so the inner
ear is not damaged.
- The inner ear
➢ Bony & membranous labyrinth:
• Bony labyrinth refers to cavities inside the
temporal bone.
• Within the bony labyrinth is the
membranous labyrinth.
• Between the 2 is a fluid called Perilymph.
• Fluid inside the membranous labyrinth is
called Endolymph.
➢ Semi-circular canals:
• 3 canals all perpendicular to each other.
• At end of each canal are ampullae.
• Inside the ampullae are cristae ampullaris, the
- Cochlea= hearing. sense organ of rotation.
- Canals = head movements. • The function of the ampulla is to detect change
- Vestibule= gravity. in direction of head, aand other head
movements
➢ Vestibule:
• Consist of the Utriculus & Sacculus.
• Within the utriculus & the Sacculus are macula.
• The macula contains receptors for changes in position of head with respect
to gravity.