D IS ORD ERS OF THE NERVO US SYSTEM
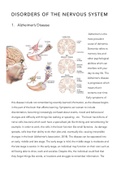
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is the
most prevalent
cause of dementia.
Dementia refers to
memory loss and
other psychological
abilities which can
interfere with your
day-to-day life. The
Alzheimer’s disease
is progressive which
means that it
worsens over time.
Early symptoms of
this disease include not remembering recently learned information, as the disease begins
in the part of the brain that affects learning. Symptoms can worsen to include
disorientation, becoming increasingly confused about events, mood and behavioural
changes and difficulty with things like walking or speaking , etc. The brain has billions of
nerve cells (neurons) which each have a specialised job like thinking and remembering for
example. In order to work, the cells in the brain function like small factories. As damage
spreads, cells lose their ability to do their jobs and, eventually die, causing irreversible
changes in the brain (Alzheimer’s Association, 2018). The disease can be separated into
an early, middle and late stage. The early stage is mild, the middle stage is moderate and
the late stage is severe. In the early stage, an individual may function on their own such as
still being able to drive, work and socialise. Despite this, the individual could feel that
they forget things like words, or locations and struggle to remember information. The
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is the
most prevalent
cause of dementia.
Dementia refers to
memory loss and
other psychological
abilities which can
interfere with your
day-to-day life. The
Alzheimer’s disease
is progressive which
means that it
worsens over time.
Early symptoms of
this disease include not remembering recently learned information, as the disease begins
in the part of the brain that affects learning. Symptoms can worsen to include
disorientation, becoming increasingly confused about events, mood and behavioural
changes and difficulty with things like walking or speaking , etc. The brain has billions of
nerve cells (neurons) which each have a specialised job like thinking and remembering for
example. In order to work, the cells in the brain function like small factories. As damage
spreads, cells lose their ability to do their jobs and, eventually die, causing irreversible
changes in the brain (Alzheimer’s Association, 2018). The disease can be separated into
an early, middle and late stage. The early stage is mild, the middle stage is moderate and
the late stage is severe. In the early stage, an individual may function on their own such as
still being able to drive, work and socialise. Despite this, the individual could feel that
they forget things like words, or locations and struggle to remember information. The